Separation force is defined as follows:
![]() , (3.26)
, (3.26)
where ![]() - coverings material density, g/sm3;
- coverings material density, g/sm3;
![]() - covering thickness, sm;
- covering thickness, sm;
![]() - the part of covering
surface area for which adhesion is estimated;
- the part of covering
surface area for which adhesion is estimated;
![]() - oscillation frequency;
- oscillation frequency;
![]() - vibrational amplitude of
the sample.
- vibrational amplitude of
the sample.
Changing frequency of ultrasonic vibrations by means of the generator, it is possible to change the separation force in a wide range. As at adhesion test in this way the direction of force action in a zone of contact periodically varies, the method do not apply to plastic substrates because of possible deformation in a contact zone.
To without inertia methods concern the separation method, separation of modular substrate element, separation of pin, longitudinal branch, shift, cut, peeling, scratching, and also vacuum method and swelling method.
Advantages of normal separation method are rather low labour input of samples manufacturing and the small charge of materials, disadvantages - necessity of application of glutinous connections that affects measurements results because of influence of own stresses in glutinous connections and penetration of glue to the substrate in case of thin porous coverings. Besides samples long time try action of stretching forces; thus in addition there are separation forces that complicates results interpretation. At use of this method loadings are limited by durability of the glue rather sensitive to technology and drying mode. The method demands a careful centering of pasted pins and alignment of acting forces for homogeneous weighting of boundary film-substrate. Some of these problems manage to be solved if to paste identical cylinders to the film and uncovered samples surface, simultaneously putting loading on axis of two cylinders.
Updating of normal separation method is the method of overturning. In this case on a pin pasted to the film, loading operates not vertically, but along boundary film-substrate. Advantage of the method in comparison with normal separation method: the applied device leaves less distortions on a substrate as loading action on substrate is partially removed; the exact centering is not required.
Peeling methods are the methods based on films separation by consecutive infringement of contact between adjoining bodies. These methods are used if film or (and) substrate is flexible. By means of special captures the film gradually pulls off the substrate; thus define either separation work, or separation force at the certain separation speed of a film.
At definition of cohesive resistance on its separation force count on unit of width of a pulled off film under the formula:
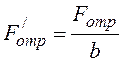 , (3.27)
, (3.27)
where ![]() - force at which the film exfoliates,
N;
- force at which the film exfoliates,
N;
![]() - width of the capture
separating films strip, m.
- width of the capture
separating films strip, m.
At measurement of cohesive resistance by peeling methods it is necessary to consider the process speed. It is necessary owing to distinction of peeling force (work) at an initial separation stage (static separation force) and during separation of film (dynamic separation force), and also because of electrostatic components presence, connected with redistribution of charges on interface film-substrate during separation. In the first case usually static separation force is greater than dynamic. In the second case with growth of separation speed and change of environments humidity in which make tests, conditions of charges "running off" in a place of separation of covering with substrate change. These processes can lead to what even at strict observance of technology of the films deposition experimentally defined separation force (work) depends on test specifications.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.