- Only 76,2 % of the sprayed material are besieged on covers.
Thus, productivity of developed installation will make 10000 covers a month. Proceeding from this, we can determine a resource of the cathode:
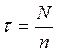 . (3.21)
. (3.21)
where N - total of the products processed during the cathode work;
n – productivity of installation in a month.
From constructive reasons we shall set thickness of the cathode: d=0,015 Then during the cathode work the quantity of the processed products will make:
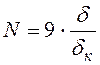 , (3.22)
, (3.22)
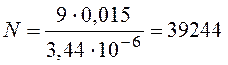 items.
items.
Finally we define the cathode resource:
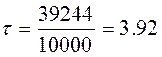 mon
=0.33 years.
mon
=0.33 years.
Development of magnetron atomizers has led to creation of planar systems in which the screening effect of the sprayed atoms stream is completely removed. The magnetic system is mounted in the water-cooled holder and does not bring pollution in the working chamber. Planar magnetron systems allow to create higher density of current in the dispersion field and to achieve sedimentation speeds, comparable with speeds, characteristic for methods of thermal evaporation in high vacuum. At the same time disadvantage of such system is that narrow annular area of target is subjected to dispersion, and, hence, low use factor of the target material.
The form of target is caused by a sprayed material sort and geometry of magnetic system. The target should provide high use factor of its material (that especially important as dispersion of a target is non-uniform, and target cost is high), good electric and thermal contacts to the water-cooled holder, convenience of replacement, minimal shielding of magnetic field.
At designing magnetron systems with flat targets most sharply there is a problem of their cooling. Significant current density on a sprayed surface lead to the non-uniform warming up of target that leads to its hogging, and in places of bad contact to the holder - to its fusion. Thus the traditional method of fastening by screws is inefficient. The greater effect gives glueing of target to the holder by means of special conductive glues, however presence of local areas of overheat at insufficient cooling can cause strong gas evolution and destruction of a glutinous layer. Reliable and effective way of fastening of targets is the soldering by means of solders of tin, indium or their alloys. At the same time fastening of targets by means of glues and solders complicates replacement of targets, and glues and solders can influence on the structure of the gas environment of vacuum working volume. Therefore more often the preference is given to those forms of a target which provide reliable thermal contact to the water-cooled holder and are easily removed.
During dispersion due to ionic bombardment the target can be warmed up to high temperature. It leads to the surface oxidation of metal targets, intensification of diffusion processes in floatable targets, to their mechanical deformation and even fusion that finally reduces process efficiency and quality of formed films. Thus, the integral element of any cathodic unit is the cooling system. In practice cathodic units both with direct cooling of target, and with indirect are widely applied. However direct cooling of target provides the highest possible efficiency of cooling and is characterized by presence of direct contact of cooling liquid with the back side of target.
Design of MAS is presented on sheet ХАИ.461.06.ДП.12.СБ.01.
The cathode-target 8 also has the form of a rectangular, reinforced in a dispersion zone. In the bottom part of unit the magnetic system consisting of a constant magnets set 3 and 4 settles down. The sprayed cathode joins to case of MRS 1. At nut 22 twisting all construction is compressed, providing tight motionless connection.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.