The maximal value of the stress acting on the anode obviously makes 258 MP.
The load factor can be defined under the formula:
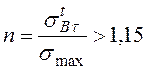 , (3.32)
, (3.32)
where ![]() – long-term strength,
– long-term strength, ![]() = 450 MP; smax – the maximal design
stress arising in the anode-collector of magnetron atomizing system at its
deformation, smax = 258 MP.
= 450 MP; smax – the maximal design
stress arising in the anode-collector of magnetron atomizing system at its
deformation, smax = 258 MP.
As a result of calculation under the formula (3.32) it is received:
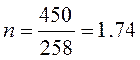
The design of the anode is chosen truly and will take acting loadings that satisfies to strength condition (3.32).
Modern data about the nature of physical and chemical processes of coverings destruction allow to formulate the basic requirements qualifying to them:
1) Coverings should create an effective barrier on a way of the gas environment atoms diffusion to the substrate and diffusion of substrate atoms through covering in the opposite direction, to have low steam tension at working temperature, poorly to interact with the substrate and environment.
2) Coverings should be compatible to a substrate: to have good coupling and have continuous duty without peeling and destructions.
3) The coordination thermophysical properties of covering and protected substrate which, first of all, is reduced to the maximal rapprochement of average values of thermal dispersion factor of condensate and protected metal for restriction of temper level in product and coverings is necessary.
4) Condensates should possess good plasticity since in conditions of variable thermal loadings they should keep the integrity.
5) From experimental data it is known, that endurance of samples depends on thickness of the besieged layer. Thus, for each solved problem it is necessary to search for the optimum thickness of the condensate.
6) Corrosion resistance of coverings and accordingly durability of protected products concern to a number of the most important requirements made to protective coatings.
The further requirements made to coverings, concern to specific and depend first of all on conditions in which the products with coverings work.
All the above described requirements are in own way important as each of them partially defines efficiency of the deposited covering.
As the reliable component should work many years in normal conditions, various methods of the accelerated tests which should provide data on expected reliability of the given component have been developed. To such tests concern temperature, under influence of moisture [19], they can be carried out separately or simultaneously.
Temperature tests are easy realized and consequently are most widely applied. According to such tests it is possible to estimate degrees of oxidation and internal changes.
For definition of protective action of covering the product put on trial on action of moisture. Such tests spend at 85 … 95оС and 85 … 95 % of relative humidity.
Question of coverings adherence with metals - the basic question of the theory and practice of protective coverings. This question has the big theoretical and practical interest. By consideration of coverings adherence with metals distinguish, as a rule, two parameters - adherence work and adherence force [20].
Adherence force of coverings with metals represents the big practical interest as a characteristic and cannot be used for quantitative calculations of the physical and chemical processes proceeding at coverings with metals formation.
Adherence work (work of adhesion), on the contrary, is the characteristic representing big scientific value. It characterizes processes and the forces led to adherence of diverse materials, can give the information on the mechanism of adherence. Knowing value of adherence work and force defining it, it is possible to calculate adherence force.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.