Existing methods of measurement and control of cohesive resistance can be classified as follows: quantitative and qualitative methods; destroying and not destroying methods; mechanical and nonmechanical methods; practical methods and the methods representing scientific interest; standard and original methods.
From all these methods most widely apply the mechanical methods based on definition of pryout work (force) of film from the surface. They are divided on two categories depending on the way of film separation: normal and longitudinal (lateral) film separation from an interface.
Almost all existing methods of adhesion research are destroying. Though it is not absolutely rational, but at the given stage of development effective enough not destroying methods of measurement of cohesive resistance of coverings with a basis are not found yet.
Mechanical methods subdivide on inertial and without inertia methods of cohesive resistance measurement. To inertial methods concern such as "bullet" method, ultracentrifugation and ultrasonic vibration method.
The kernel of "bullet" method consists in that the sample - substrate of the special form with the deposited covering goes-off by the adaptation in direction of a braking target. During the moment of impact of target and covering inertia, normal to interface and proportional to braking acceleration at impact operates. This force on unit of the contact surface area of covering with substrate is equal:
![]() , (3.24)
, (3.24)
where ![]() - covering materials density, g/sm3;
- covering materials density, g/sm3;
![]() - covering thickness, sm;
- covering thickness, sm;
![]() - braking acceleration, m/s2.
- braking acceleration, m/s2.
The Given method is expedient for using, when functional purpose of covering for products as a whole provides operation in overload conditions. This way allows to develop braking acceleration up to 104 m/s2.
The ultracentrifugation method is based on a principle of the sample with covering rotation. The sample from ferromagnetic in the form of the cylinder-rotor, on forming surface of which the covering is deposited, place in the vacuum chamber; here the sample rotates with the big speed around of axis in a rotating magnetic field. The stresses developing under action of centrifugal forces are directed along radius in section of the cylinder and are perpendicular to border of section:
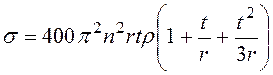 , (3.25)
, (3.25)
where ![]() - rotation frequency of rotor, s-1;
- rotation frequency of rotor, s-1;
![]() - rotor radius, sm;
- rotor radius, sm;
![]() - film thickness, sm;
- film thickness, sm;
![]() - coverings material
density, g/sm3.
- coverings material
density, g/sm3.
The cohesive
resistance corresponds to the separation stress at frequency of rotation
![]() .
.
At carrying out of tests smoothly increase rotation frequency of rotor
and fix value ![]() at which the film comes off from the
basis. The rotation frequency necessary for separation
of continuous
film, depends on its tension stress, cohesive resistance. For elimination of
hoopential stress the film is cut in parallel with rotor axes so that to divide
the layer into a number of strips.
at which the film comes off from the
basis. The rotation frequency necessary for separation
of continuous
film, depends on its tension stress, cohesive resistance. For elimination of
hoopential stress the film is cut in parallel with rotor axes so that to divide
the layer into a number of strips.
Advantages of the given method are absence of glue, perpendicularity of separation forces to boundary covering-basis. These advantages of the method are really very important; however there are disadvantages which limit its application - the difficult hardware registration, the special form of samples, interrelation of rotation frequency and durability of the rotor-substrate material. Because of small weight of thin films it is difficult to receive big centrifugal forces.
One of
inertial methods also is the method of cohesive resistance measurement using
vibrations. The sample together with covering is exposed to ultrasonic
fluctuations. Thus on covering operates separation force ![]() , reaching maximum
at
measurement of the sample with the covering movement direction in an ultrasonic
field, and the pressing force operating in the following half-cycle.
, reaching maximum
at
measurement of the sample with the covering movement direction in an ultrasonic
field, and the pressing force operating in the following half-cycle.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.