3) Area of high values of the magnetic induction (> 0.06 Tl), value of the parameter a(b) is smoothly reduced under the law close to linear with growth of value of the magnetic induction.
Similar division of dependence a(b)=f (B) allows to interpolate it and use for manual or machine definition of the discharge characteristics of magnetron sputtering systems at calculation of parameter a(b). Also it will be used in the technique for definition of thermal mode of a substrate at drawing coverings with the help of magnetron sputtering systems.
Rather wide range of working voltage 300 … 700 V is used in magnetron sputtering systems. The specified borders are rather conditional and depend on lines of parameters (working pressure, a material of working gas and a sprayed material, values of the induction of the magnetic field, etc.).
The bottom border of the range is defined by striking voltage of the abnormal glow discharge [20, 23, 27, 29]. In figure 8.8 experimental dependence of striking voltage of the abnormal glow discharge is resulted. Researches have shown, that dependences of striking voltage on pressure of working gas and an induction of a magnetic field are similar. Similarity of the resulted dependences specifies that fact, that the magnetic field and working pressure render identical influence on occurrence and development of the discharge in magnetron sputtering systems.
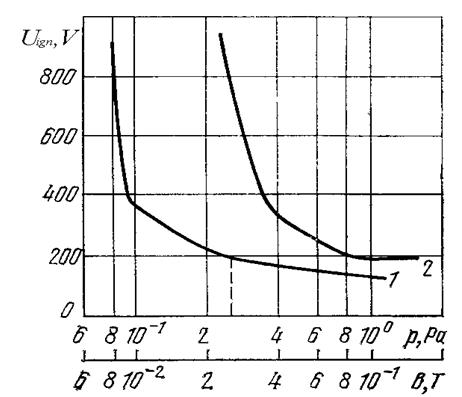
Figure 8.8 Dependence of striking voltage on pressure at a constant induction of a magnetic field 0,06 Tl (a curve 1) and an induction of a magnetic field at constant pressure (a curve 2)
The analysis of the resulted dependences shows, that it is possible to divide dependences Uз (В), and Uз (р) into three zones:
1) Area of practically constant values of striking voltage at change of working pressure and induction of the magnetic field (р> 0.25 Pa, В> 0.1 TL);
2) Area of linear growth of values of striking voltage of the discharge in a range of allowable working values of pressure and induction of the magnetic field (р=0.09 … 0.25, В=0.03 … 0.1);
3) Area of sharp growth of value of striking voltage of the discharge at decreasing of pressure and induction of the magnetic field (р <0.09, B <0.03). As values of pressure and induction of the magnetic field fall outside the limits of allowable values this area interests us a little.
In [39] authors suggest to accept for calculation U0=250 V, however having foregoing dependences it is possible to determine striking voltage of the discharge more precisely depending on working pressure and induction of the magnetic field.
Also with the help of experimental researches it has been established, that value of parameter<σoVe> makes 10-12 m3/s.
One of the main disadvantages of the given model of the processes occurring in magnetron sputtering systems is one-dimensionality of the considered problem. As it is known, the density of plasma, and, hence, the density of the current on the cathode - target changes along field lines of the magnetic field. In the central part of plasma area (lines of the magnetic field are parallel with a cathode - target surface) the density of ions is maximal, and on periphery (lines of the magnetic field are almost perpendicular to cathode - target surface) density of ions is much smaller, process of dispersion is practically absent. Presence of similar distribution of particles on density and on energies along field lines of the magnetic field would allow to determine density of the current on the cathode - target with high accuracy, speed of dispersion of the target surface in each point, change of geometry of the cathode - target during dispersion, and also determine with high accuracy uniformity of the received covering. However, at present it was not possible to describe the listed processes by analytical expressions. In works [2, 3, 5, 7] is offered the numerical modeling of the charged particles movement in electric and magnetic fields. The given model will be considered in the corresponding section.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.