Performances reported by SC1 board include: output optical power, laser working temperature, bias current and ambient temperature.
3.4.2 Dual Directional Optical Supervising Channel Unit
SC2 board can process the signals of two optical supervisory channels so as to meet the requirements for bi-directional receiving and transmitting of the optical supervisory signals at the optical relay station. The hardware principle, functions, application and alarms of SC2 board are basically the same as those of SC1 board, except that one path of optical port is added for processing, so further explanation is omitted here. But the following two points have to be emphasized:
n Whether SC1 board itself is good or not can be judged by self loop of "RM" and "TM" optical ports with optical fiber jumper to see whether there is any alarm, and this method is also applicable to SC2 board. But since SC2 has the optical signals from two directions, when self loop method is used to judge SC2 board, two fiber jumpers must be used to short circuit the receiving/transmitting ports in two directions respectively. Then judge whether there is any alarm of the board and locate the board fault.
n The optical ports "RM1" and "TM1" as well as "RM2" and "TM2" on SC2 handle bar correspond to each other one by one. Please pay enough attention to the flow direction of the optical supervisory signals.
3.4.3 Optical Supervisory Channel Access Unit
At the optical transmitting end, the main channel of OptiX BWS 320G system and optical supervisory channel are multiplexed by SCA board and enter into one optical fiber; while at the receiving end, the main channel and optical supervisory channel transmitted in one optical fiber are demultiplexed by SCA board for further processing respectively.
1. Principle
The essential part of SCA board is an optical multiplexer for wavelength-division multiplex (WDM) and an optical demultiplexer for wavelength-division demultiplex, the principle is shown in Figure 3-18.
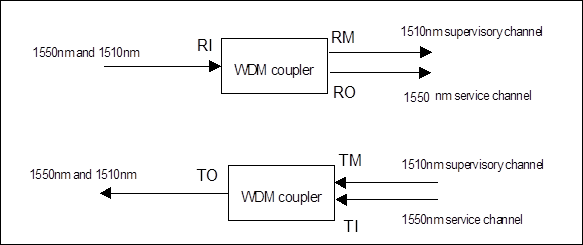
Figure 3-18 Principle block diagram of optical supervisory channel access board SCA
The optical signals sent from the opposite end enter SCA board from "R1" optical port on the handle bar and divided into two parts by the optical demultiplexer: one part is the service main channel of WDM, with carrier wavelength as 1550nm, and output from "RO" port of SCA board; the other part is the optical supervisory channel at wavelength of 1510 and output from "RM" port of SCA board. These two parts of optical signals are sent to corresponding boards for processing. At the local station, the supervisory channel optical signals sent from optical supervisory board SC1 or SC2 and input from "TM" interface (wavelength 1510nm) and the main channel optical signals sent from the optical amplifier board and input from "TI" interface are multiplexed by the optical multiplexer of SCA board and enter into one line optical fiber from "TO" port for transmission to the opposite end.
2. Functions
SCA board is mainly composed of two optical passive devices. Its function is to multiplex or demultiplex the main channel and the optical supervisory channel. The reason why SCA board is designed separately is that thanks to the function of SCA, the main channel and the optical supervisory channel can be independent of each other and do not affect each other. When local fault occurs to the system, if it is the problem of the optical supervisory channel, the optical supervisory channel processing board SC1 or SC2 can be directly replaced without affecting the services on the main channel; similarly, if the main channel is faulty, the optical amplifier board or optical wavelength conversion board can be replaced without affecting the orderwire calls and NM information transmitted on the optical supervisory channel.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.