pause % Strike any key to design the network...
% DEFINE THE NETWORK
% ==================
% NEWLIN generates a linear network.
% We will use a learning rate of 0.1, and five
% delays in the input. The resulting network
% will predict the next value of the target signal
% using the last five values of the target.
lr = 0.1;
delays = [1 2 3 4 5];
net = newlin(P,1,delays,lr);
pause % Strike any key to adapt the linear neuron...
% ADAPTING THE LINEAR NEURON
% ==========================
% ADAPT simulates adaptive linear neurons. It takes the initial
% network, an input signal, and a target signal,
% and filters the signal adaptively. The output signal and
% the error signal are returned, along with new network.
% Adapting begins...please wait...
[net,y,e]=adapt(net,P,T);
% ...and finishes.
pause % Strike any key to see the output signal...
% PLOTTING THE OUTPUT SIGNAL
% ==========================
% Here the output signal of the linear neuron is plotted
% with the target signal.
plot(time,cat(2,y{:}),time,cat(2,T{:}),'--')
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Output --- Target - -');
title('Output and Target Signals');
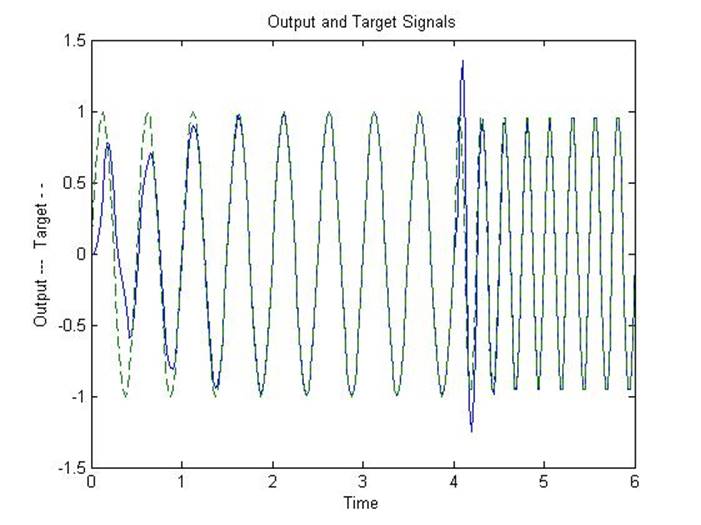
% It does not take the adaptive neuron long to figure out
% how to generate the target signal.
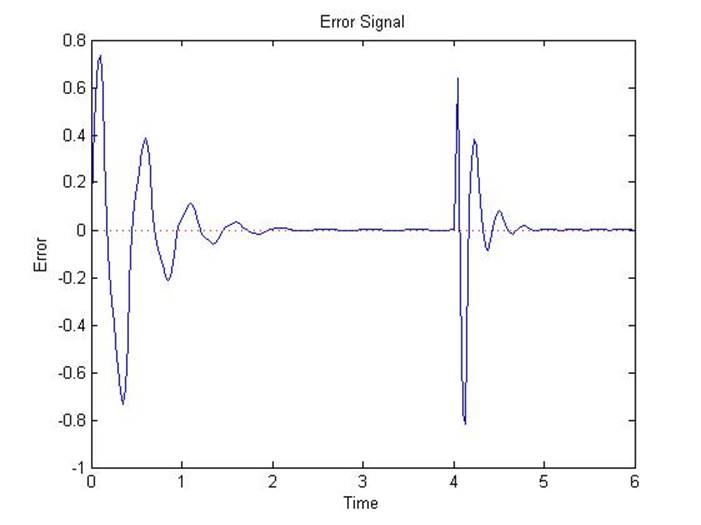
pause % Strike any key to see the error signal...
% A plot of the difference between the neurons output
% signal and the target signal shows how well the
% adaptive neuron works.
plot(time,cat(2,e{:}),[min(time) max(time)],[0 0],':r')
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Error');
title('Error Signal');
echo off
End of APPLIN2
2.9.3. Elman amplitude detection
Сети Эльмана могут быть обучены распознавать и воспроизводить как пространственные, так и временные структуры. Примером задачи, в которой временные структуры распознаются и сопоставляются с пространственной структурой является обнаружение амплитуды.
Распознавание амплитуды требует, чтобы сигнал был представлен во времени, а также, чтобы на выходе сети была амплитуда сигнала. Это несложная проблема, но она иллюстрирует процесс проектирования сети Эльмана.
% NEWELM - Inititializes an Elman recurrent network.
% SIM - Simulates an Elman recurrent network.
% TRAIN - Trains an Elman recurrent network.
% AMPLITUDE DETECTION:
% Using the above functions an Elman network is trained
% to output the amplitude of a sine wave being presented
% in time.
pause % Strike any key to continue...
% DEFINING THE PROBLEM
% ====================
% The first wave form has an amplitude of 1.
p1 = sin(1:20); % If input is wave with amplitude of 1
t1 = ones(1,20); % then output should be 1
% The second wave form has an amplitude of 2.
p2 = sin(1:20)*2; % If input is wave with amplitude of 2
t2 = ones(1,20)*2; % then output should be 2
% The network will be trained on the sequence formed by
% repeating each wave form twice.
p = [p1 p2 p1 p2];
t = [t1 t2 t1 t2];
Pseq = con2seq(p);
Tseq = con2seq(t);
pause % Strike any key to define the Elman network...
% DEFINE THE EHLMAN NETWORK
% =========================
% The function NEWELM creates an Elman network whose input
% varies from -2 to 2, and has 10 hidden neurons and 1 output.
net = newelm([-2 2],[10 1],{'tansig','purelin'},'traingdx');
Warning: NEWELM used in an obsolete way.
> In nntobsu at 18
In newelm at 98
In appelm1 at 51
See help for NEWELM to update calls to the new argument list.
net.trainParam.epochs = 500;
net.trainParam.show = 5;
net.trainParam.goal = 0.01;
pause % Strike any key to train the Elman network...
% TRAINING THE ELMAN NETWORK
% ===========================
% TRAIN trains Elman networks. Here it is trained
% without training parameters. (The default will be used.)
% Training begins...please wait, this takes a while...
tic
[net,tr] = train(net,Pseq,Tseq);
toc
Elapsed time is 24.154738 seconds.
% ...training done.
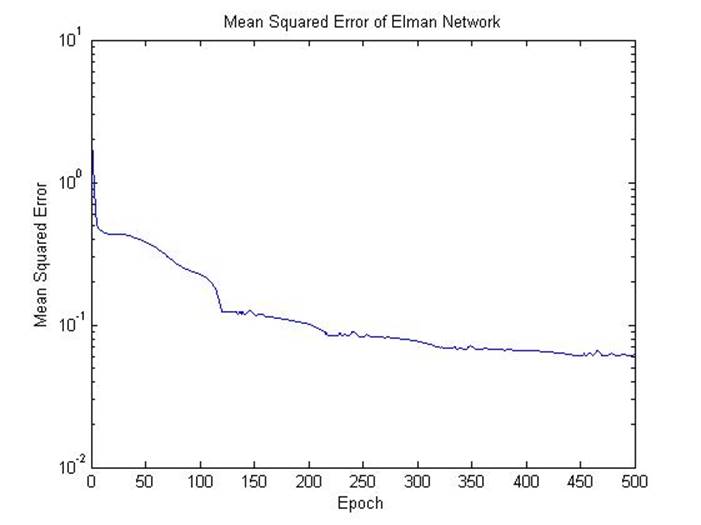
semilogy(tr.epoch,tr.perf)
title('Mean Squared Error of Elman Network')
xlabel('Epoch')
ylabel('Mean Squared Error')
pause % Strike any key to test the Elman network...
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.