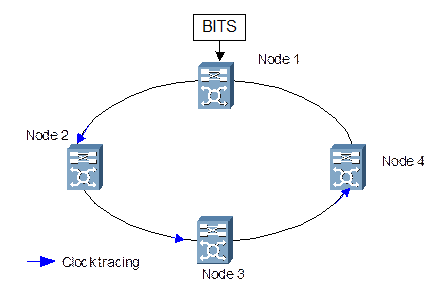
Figure 2-5 Networking of clock with SSM not enabled
If there is fiber break in the loop, the clock will be traced mutually, as shown in Figure 2-6.
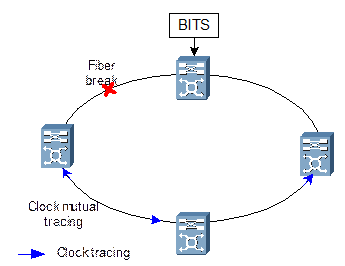
Figure 2-6 Clock mutual tracing caused by fiber break
2.7.2 Clock Configuration with SSM Enabled
SSM, a mechanism for synchronization management in SDH network, allows switching the quality information of clock source among nodes. Thus, the OptiX OSN 9500 can automatically choose the clock source of the highest quality and priority to prevent the occurrence of clock ring, as shown in Figure 2-7. SSM is loaded in the lower four-digit bit of S1 byte in SDH line overhead.
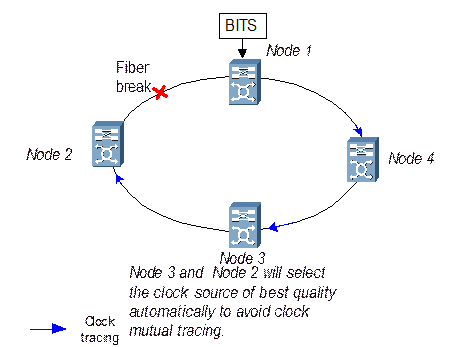
Figure 2-7 SSM application
However, SSM cannot avoid the clock ring completely, as shown in Figure 2-8. Huawei raises the concept of clock source ID, which is defined using the higher four-digit bit of S1 byte and transmitted with SSM. When a node receives the S1 byte, it checks the clock source ID to judge whether it is originated from this station. If so, the clock source is unavailable, thus the clock ring can be avoided, as shown in Figure 2-9.
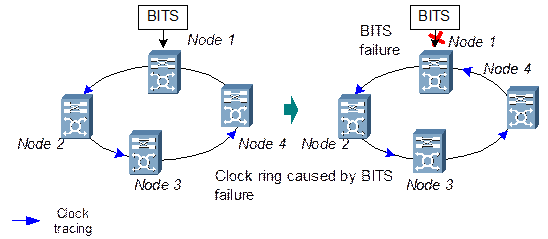
Figure 2-8 Clock ring occurs when enabling SSM
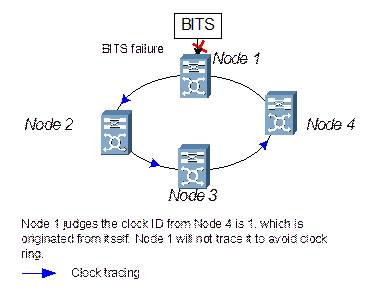
Figure 2-9 Application of clock source ID
A clock ID can be allocated by NM or set manually. In an SDH ring network, the clock ID is usually set manually to effectively prevent the occurrence of timing ring. Only some key NEs in the SDH network need the clock source ID, set the clock ID following these rules:
n Allocate the clock ID for all external BITS.
n Allocate clock ID for the internal clock source of node with external BITS.
n Allocate clock ID for the internal clock source of the junction node of a ring and chain or two rings.
n For a junction node, if the clock tracing level includes ring clock source, allocate clock ID for this clock source.
2.7.3 Examples of Clock Configuration
Here introduces the clock configuration in chain network, intersecting ring and tangent ring networks.
1. Clock Configuration in Chain Network
Clock interlock will not occur to a chain network that enables SSM. If there are more than 20 nodes, a BITS clock should be added for compensation, as shown in Figure 2-10.
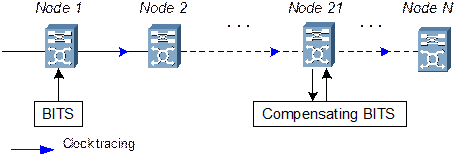
Figure 2-10 Clock configuration in chain network
2. Clock Configuration in Intersecting Ring Network
The clock configured in an intersecting ring network is shown in Figure 2-11.
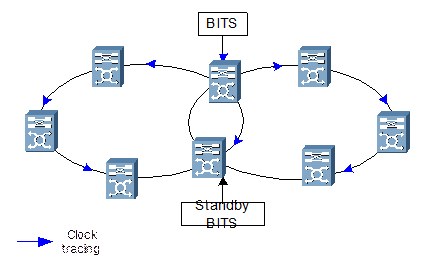
Figure 2-11 Clock configuration in intersecting ring network
3. Clock Configuration in Tangent Ring Network
The clock configured in a tangent ring network is shown in Figure 2-12.
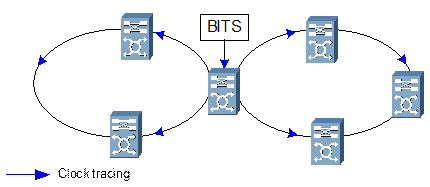
Figure 2-12 Clock configuration in tangent ring network
2.8 Auxiliary Interface Configuration Requirement
The OptiX OSN 9500 provides serial ports Serial 1, Serial 2, Serial 3 and Serial 4 (hereinafter called S1, S2, S3, S4), with the functions listed in Table 2-20.
Table 2-20 Functions of serial ports S1–S4
|
Serial port |
Electrical standard |
Rate |
Functions |
Configuration mode |
|
S1–S4 |
RS232/RS422 |
19.2 kbit/s |
Environment monitoring, microwave monitoring |
Point to point, broadcast |
Figure 2-13 shows a case of environment and microwave monitoring using S1–S4.
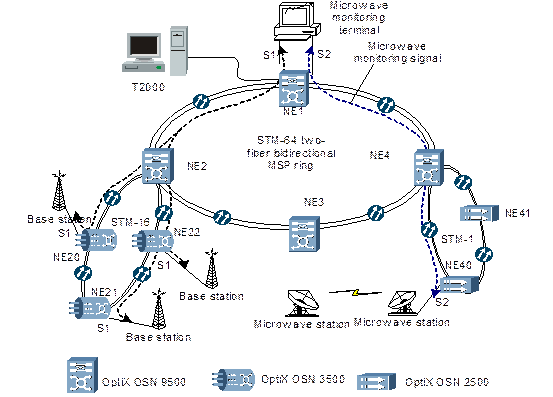
Figure 2-13 Auxiliary interface configuration
S2 is configured as point-to-point mode to monitor the microwave stations. S1 is configured as broadcast mode. The S1 of NE1 sends broadcasting, upon receiving the broadcasting, NE20, NE21, NE22 will return the value of environment they monitor.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.