The straight-through cutting tool with the tips produced from the hard alloy is selected according to the GOST 18878-73 [10, p.123, table.13] (ref. fig.2.3).
|
|
|
fig. 2.3 |
The geometric characteristics are filled in the table #2.4.
Table #2.4
|
Cutter |
h, mm |
b, mm |
L, mm |
n, mm |
l, mm |
R, mm |
φ |
φ 1 |
|
The straight-through cutter Т5К10 GOST 18887-73 |
25 |
16 |
140 |
9 |
12 |
1.0 |
60 |
45 |
2.7.3 The calculation of cutting process parameters
Calculation of the cutting process for surface # 8 is the following:
The nominal allowance for machining according table #2.2 is following
![]() , so
, so 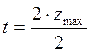
![]() .
.
The feed will be chosen with the help
of diagram 14 [10, p.268]. It depends on the required roughness of machining
and the radius of the cutter top. This surface is performed with Rz = 80 ![]() and radius R = 1mm, thus the feed is equal
to S = 0,36 mm/rev.
and radius R = 1mm, thus the feed is equal
to S = 0,36 mm/rev.
The feed is more than 0.2, so the cutting velocity will be calculated as following:
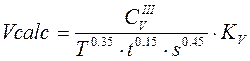 , (2.11)
, (2.11)
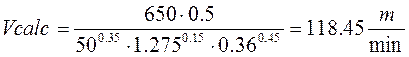
where
T=60 min; t= 1.275 mm; ![]() =650
=650
КV=КMV*КRV*КTV*КφV (КφV – the coefficient that shows the influence of cutter parameters [10,p.271,table.18]).
The correction factor КMV keeps in mind the influence of physical and mechanical material properties КMV=0.5
According to the table #5 [10,p.263] the correction factor КRV was defined. This factor takes into account the influence of a blank surface condition. This surface has already been machined, so КRV=1.
The correction factor КTV keep in mind the influence of the cutting tool material, so КTV =1 because the machining is performed by the cutter that are produced from the hard alloy.
The correction factor КφV – the coefficient that shows the influence of cutter parameters [10,p.271,table.18]), КφV =1
Thus КV=0.5*1*1*1=0.5.
The force that exists when the cutting is performed can be calculated by the following formula:
![]() (2.12)
(2.12)
Thus, ![]()
The torsion moment is calculated by the following formula:
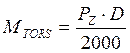 (2.13)
(2.13)
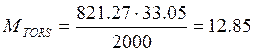 (
(![]() )
)
The power of spindle lathe is calculated by the following formula:
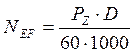 (2.14)
(2.14)
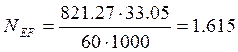 (
(![]() )
)
Let’s calculate of frequency rotation of lathe spindle by the following formula:
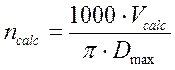 (2.15)
(2.15)
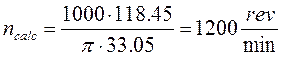
2.7.4 Selection of machine
The semiautomatic, screw-cutting lathe 16B16A is chosen for this operation. It is because we have small scale production.
The technical characteristic [10, p.13, table.7]:
· The rotational frequency spindle is 20; 25; 31; 39; 48; 61; 76;95; 119; 149; 186;232; 291; 363; 454; 568; 710; 888; 1110; 1387; 1734 rev/min;
· Longitudinal feed tool box is 0.01-0.7 mm/rev;
· Transversal feed tool box is 0.005-0.35;
· The power of electric motor transmission is 2.8 kW.
The part is fixed with the help of three-jaw chuck.
The
rotational frequency of lathe spindle 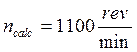 is selected in the lathe passport
and the actual feed is adopted S = 0.33 mm/rev. If we have the other value of
rotational frequency we are to recalculate
is selected in the lathe passport
and the actual feed is adopted S = 0.33 mm/rev. If we have the other value of
rotational frequency we are to recalculate![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
So the actual cutting velocity is defined by the following formula:
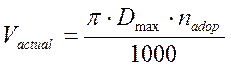 (2.16)
(2.16)
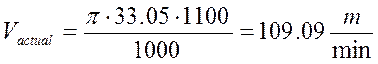
The force that exists when the cutting is performed by the following formula:
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.