CSTR: Reaction Rate Kinetics
The Problem Statement:
Reaction:
Decomposition of di-t-butyl peroxide (DTBP) to acetone and ethane
![]()
Reaction kinetics:
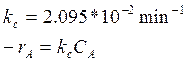
Reaction conditions:
Temperature 154.6 oC
Pressure 491.8 mmHg
Feed and initial conditions:
100 kmol/h of (DTBP) at 110 oC and 760 mmHg
Information for steady state:
Perform a simulation to determine the volume of the reactor at steady state to achieve the desired conversion, the steady state heat duty and the steady-state mole rates of components in the product stream.
Procedure:
Step 1: Creating the Flow sheet
Step 2: Formatting Engineering Units and Selecting Components
Step 3: Entering the feed stream composition
Step 4: Entering the reactor specs
Step 5: Running the simulation and retrieving the results
From the File menu select New, save to desired directory. Select and click the kinetic reactor, feed and product icons on the workspace. Connect the three using the stream icon.
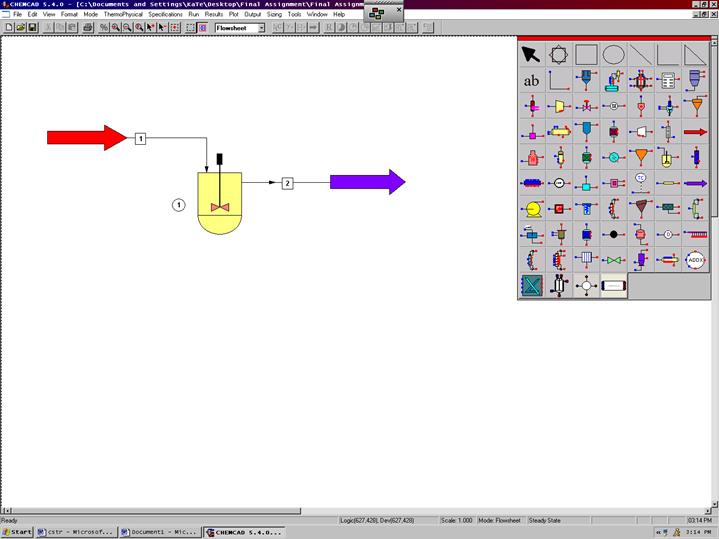
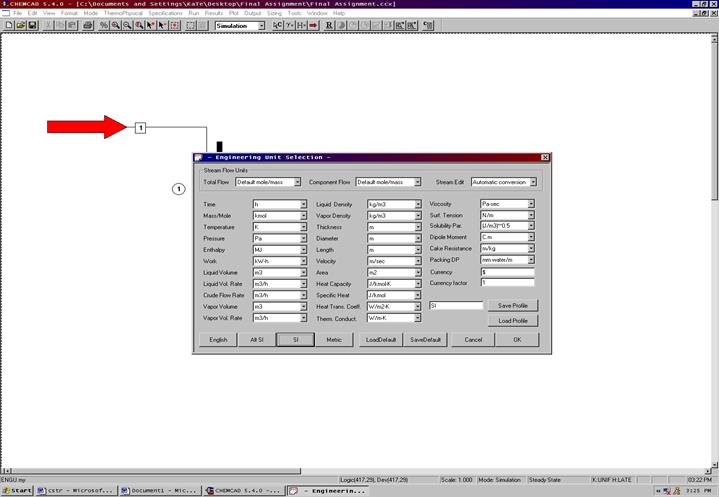
At the top of the screen change the scroll down menu from Flowsheet to Simulation. Go to the Format menu and select Engineering Units. Use the SI option at the bottom to convert all units at the same time. The desired units for each category may also be selected individually. Click OK to continue.
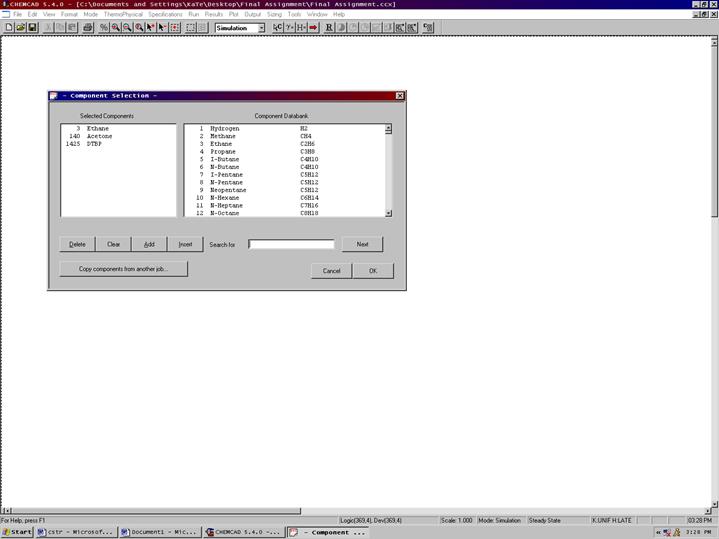
Next Go to Thermophysical on the menu bar and click on Components List. Find DTBP (Di tertiary butyl peroxide), acetone, and ethane from the CHEMCAD components list and add them to the component list. Click OK to continue.
The Thermodynamics Wizard will then appear, enter the desired information. Click OK to Continue. The K-Value Wizard can be accessed any time by clicking on the Thermophysical menu and then scrolling down to K-Value Wizard. Click OK. On the second screen select the SRK equation of state if the UNIFAC equation of state does not work. Click OK.
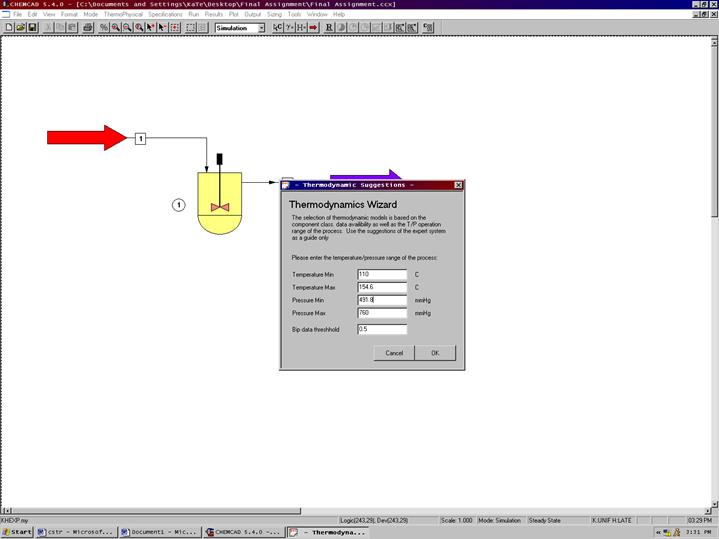
Step 3: Entering the feed stream composition
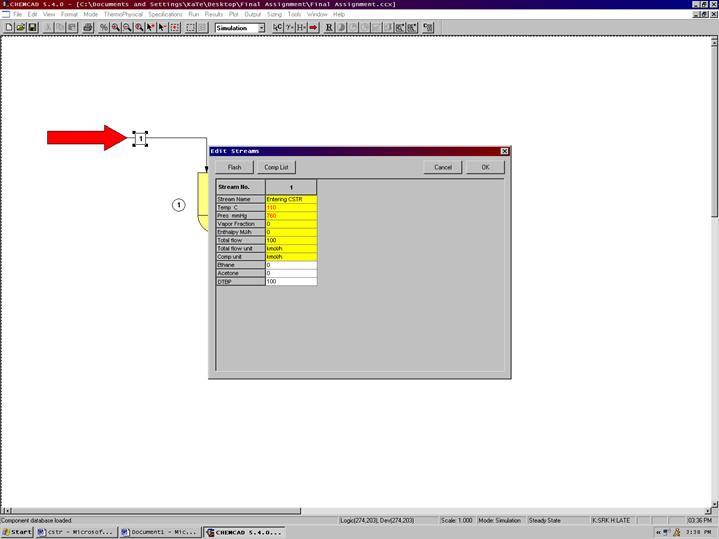
Double click on the feed stream and enter the feed information (temperature, pressure, total flow rate and component mole fractions) given in the problem statement. Click once on Flash to get the feed stream enthalpy and vapor fraction in feed at the feed conditions. Click OK. Click on the Exit stream and input the isothermal temperature and pressure. Click Flash. Click OK.
Double click on the reactor.
General Specifications Page:
Number of reactions: As there is only one reaction in the problem statement, enter ‘1’
Reactor Pressure: Enter the reactor pressure as given in the problem statement (491.8 mmHg)
Pressure Drop: As there is no pressure drop specified within the reactor. Leave this blank.
Kinetic Rate Expression: There are two options for this. The default option (Standard) is used when the rate equation is in standard Arrhenius form. The other option (User Specified) is used when the rate law is not in its standard form and the user needs to enter this manually. For more information on this, the user can always click on the help button that appears at the bottom left corner on this page. For this problem, the kinetic rate expression is given to the user. So, the User Specified option should be selected.
Reaction Phase: As the reactant, DTBP and one product, ethane, are in vapor phase at reaction pressure and temperature and the other product, acetone is in liquid phase, Vapor Reaction, Mixed Phase radio button should be selected.
Specify Reactor Type: As the reactor described in the problem statement is a CSTR, CSTR should be selected form the drop box.
Thermal Mode: As the temperature of the reaction is given as 154.6 oC, Isothermal option should be selected.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.