The cell physiology.
By OLEGarh
THE PLAN OF LECTURE:
-
Cell as an open system.
-
The organization of streams of energy, substance and the information.
-
Life cycle of a cell.
-
Autoreproduction of cells. Types of the cell divisions (classification).
-
Cellular proliferation and its value for medicine.
By OLEGarh
Types of systems by the form an exchange of substance or energy:
-
Isolated
-
Adiabatic
-
Closed
-
Open systems - any exchange of substance and energy is possible .
By OLEGarh
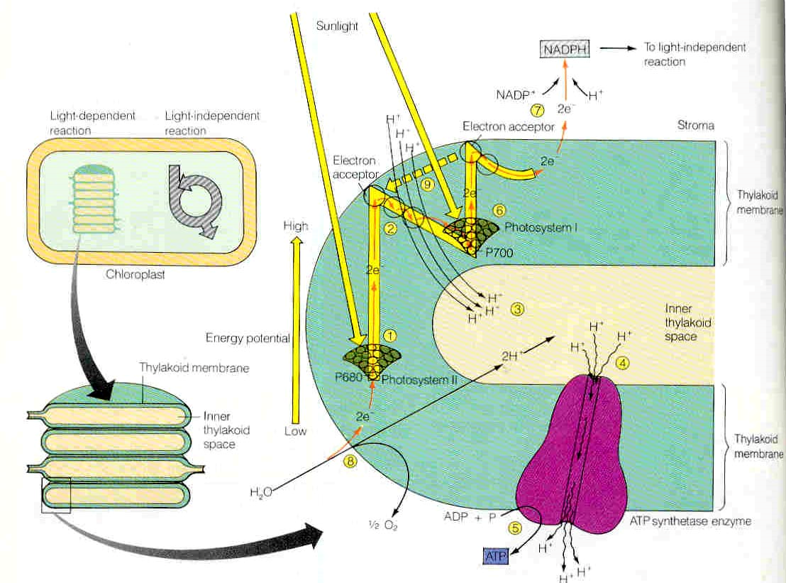
The photosynthesis.
By OLEGarh
Oxygen stage of a power exchange.
photosynthesis
С6Н12О6
АТP
NADPН2
Energy
of
electron
Solar
energy
fermentation
breath
2PVC+2АТP
electrontransport
chain
34АТP
2АТP
6СО2
8 NADP Н2
2FADН2
By OLEGarh
Plastic exchange.
-
photosynthesis;
-
6СО2 + 6Н2О -> С6Н12О6 + 6О2
-
chemosynthesis;
-
H2S + O2 > H2O + S + Q
-
NH3 + O2 > H2NO3 + Q
-
biosynthesis of proteins;
-
protein---> amino acid---> own protein.
By OLEGarh
Synthesis of proteins.
-
Activization of amino acid by specific enzyme at presence АТP with formation of aminoaciladenilate.
-
Connection of the activated amino acid to specific t-RNA with liberation of AMP.
-
Linkage of aminoacil t-RNA (t-RNA with the loaded amino acid) with ribosomes and inclusion of amino acids in the protein with liberation t-RNA .
By OLEGarh
-
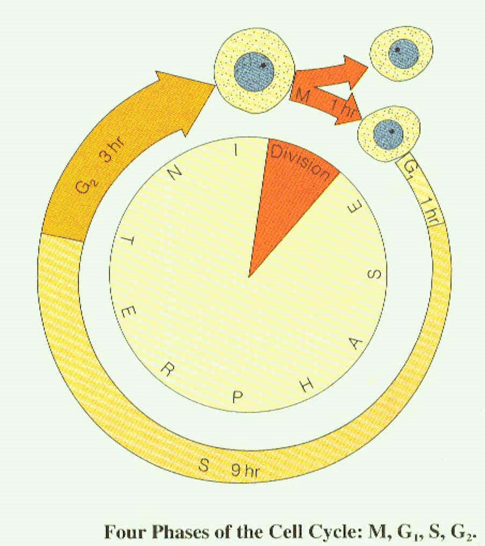
The period of time from the ending of one division up to the end the following divisions name life cycle (or cellular).
By OLEGarh
The periods in life cycle of a cell
-
the period between divisions - interphase when the cell grows, functions, is prepared for division;
-
division of a cell - mitosis.
By OLEGarh
The periods of interphase.
-
Postmitotic, or presynthetic period G1.
-
Synthetic period S. 2n 2chr. 4С
-
Postsynthetic, or premitotic period G2. 2n 2chr. 4С
By OLEGarh
DIVISION of the CELLS
MITOSIS AMITOTIC DIVISION
1. actually mitosis by the form by the type
2. Meiosis
3. Endomitosis 1. Equal 1. Generative
4. Polyteny. 2. Non-equal 2. Reactive
3. Fragmentation 3. Degenerative
4. Without cytotomy
By OLEGarh
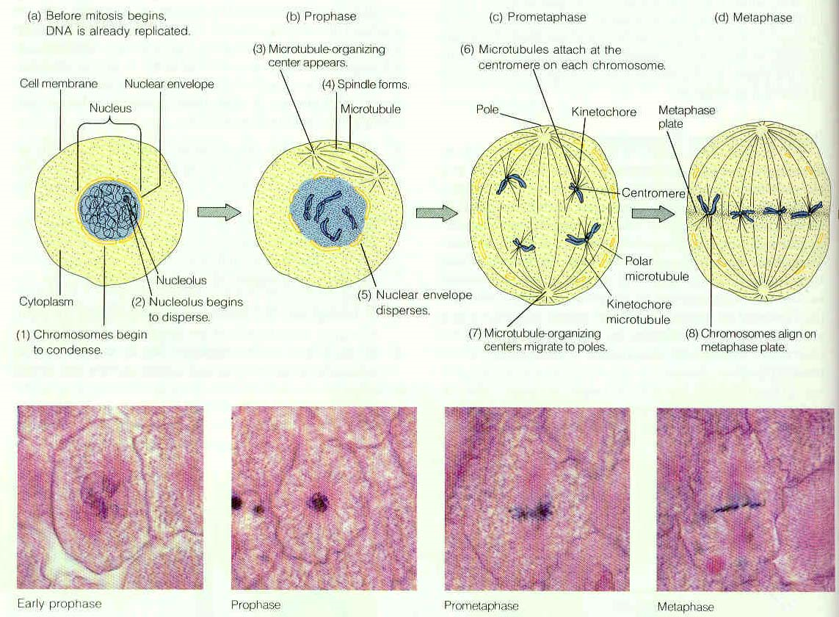
MITOSIS
By OLEGarh
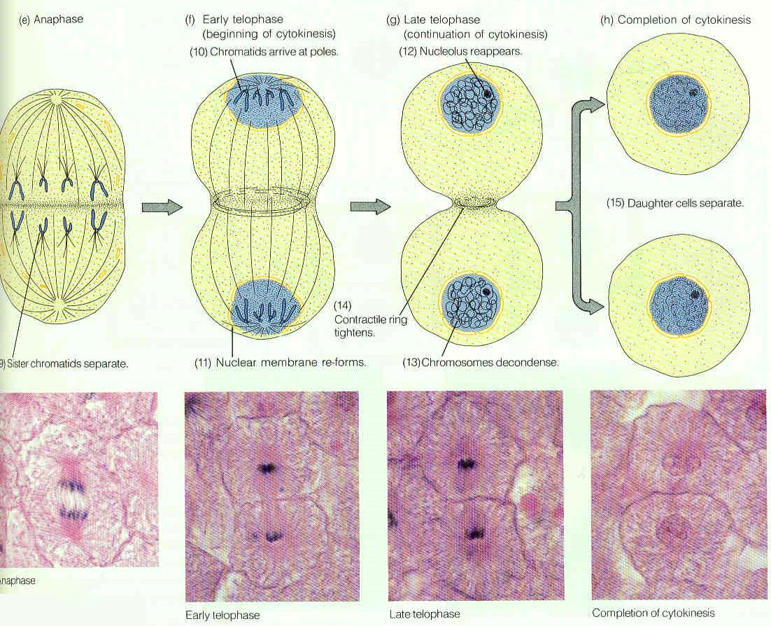
MITOSIS
By OLEGarh
Phases of mitosis:
-
prophase,
-
prometaphase,
-
metaphase,
-
anaphase,
-
telophase.
By OLEGarh
Value of mitosis.
-
Provides continuity of chromosomes in a number of cellular generations and uniform their distribution in daughter cells.
-
The universal mechanism of reproduction of the cellular organization eukariotes.
-
Genetic continuity, formation identical with parent daughter cells.
-
Growth of an organism.
-
Regeneration.
-
Cellular proliferation.
By OLEGarh
-
Endomitosis - occuring chromosome replication without cell division
-
Polyteny - reproducing of chromonemms in chromosomes without increasing the chromosome number (up to 1000 and more times).
-
Amitotic division - nuclear fission without spiralisation of chromosomes and without formation of the mitotic apparatus.
By OLEGarh
Kinds of amitotic division:
-
generative,
-
reactive,
-
degenerative.
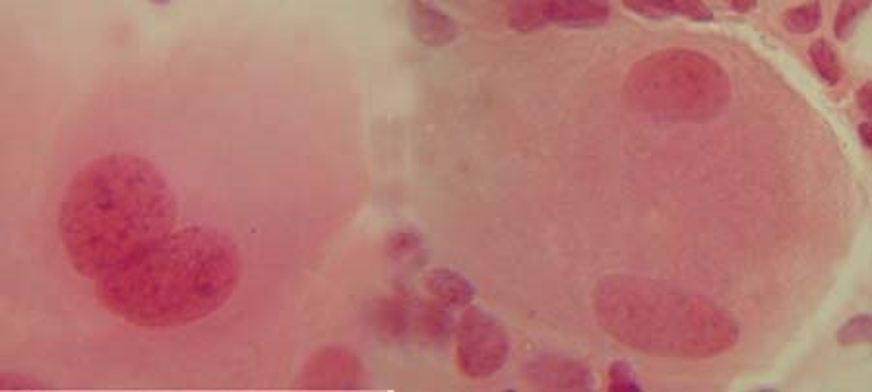
By OLEGarh
Nuclear fission at amitotic division.
-
Uniform
-
Non-uniform
-
Fragmentation
By OLEGarh
Three groups of the cellular proliferation:
-
Labile
-
Stable
-
Static.
By OLEGarh
MEIOSIS
1-reducing (Meiosis 1), 2-equalizing (Meiosis 2)
Meiosis 1
Prophase 1 - 5 stages:
leptonemm
zygonemm
pahynemm
diplonemm
diakinesis
Metaphase 1
Anaphase 1
Telophase 1
Meiosis 2
Prophase 2
Metaphase 2
Anaphase 2
Telophase 2
By OLEGarh
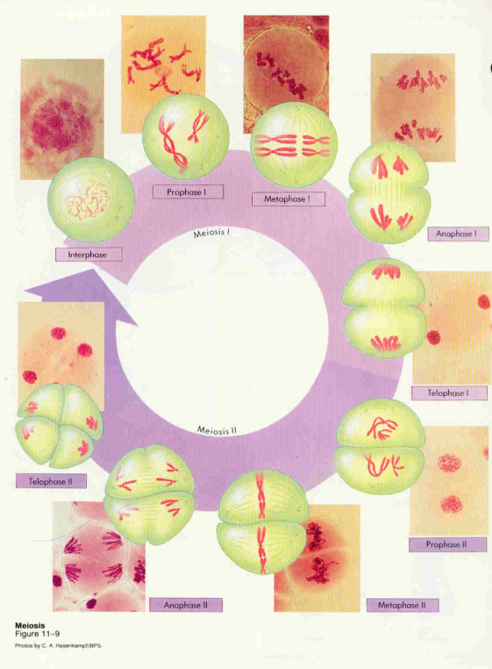
meiosis
By OLEGarh
Value of meiosis.
-
Provides formation of sexual cells.
-
Promotes maintenance of a constancy of number of chromosomes.
-
Causes a plenty of new combinations chromosomes.
-
Forms a plenty combination genes.
-
Is a source of combinative diversity.
By OLEGarh
Thanks for attention.
By OLEGarh





