Figure A-12 gives an example of orderwire configuration.
Figure A-12 Orderwire configuration
The ECC configuration should follow the requirements listed in Table A-19.
Table A-19 Configuration requirements of ECC
|
No. |
ECC configuration requirement |
|
1 |
Disable unnecessary ECC channels according to the number limit of equipment ECC. |
|
2 |
Use multiple gateway nodes to manage a large number of nodes. |
|
3 |
Usually, no ECC manual routing is necessary. |
|
4 |
In the case that no optical path is available between nodes, set the extension ECC using an Ethernet cable. |
Table A-20 shows the clock configuration requirements.
Table A-20 Clock configuration requirements
|
No. |
Clock configuration requirement |
|
1 |
The central node or a node of high reliability should provide the clock source. |
|
2 |
If there is a building integrated timing supply system (BITS) or other external clock equipment of high precision, the NE is recommended to adopt the external timing mode; if not, the line timing is recommended. The internal timing should be taken as the lowest level of clock tracing. |
|
3 |
Try to avoid the mutual tracing between NEs: If an NE does not enable the SSM function, the east and west clocks in one system of the NE cannot be both configured as clock tracing level. If the NE enables SSM, the above said clocks can be configured as clock tracing level. Note to avoid mutual tracing by proper planning and setting clock subnet ID. |
|
4 |
The line clock tracing should follow the shortest path: In a ring network comprises of less than six NEs, the reference clock can be traced from one direction. In a ring network comprises of no less than six NEs, the line clock should trace along the shortest path. For example, if there are N NEs, half of them trace the reference clock in one direction and the other half trace the reference clock in the other direction. |
|
5 |
Provide clock compensation for long clock chain: The number of G.812 slave clocks in the transmission link should be no more than 10; the number of G.813 clocks between G.812 slave clocks should be no more than 20, and the total number of G.813 clocks should be no more than 60. |
|
6 |
Allocate the clock ID properly to avoid any clock mutual tracing. |
The clock of the OptiX OSN 3500 can be configured as:
n synchronization status message (SSM) disabled
n standard SSM enabled
n extension SSM enabled
Here, the OptiX OSN 3500 selects and switches the clock source according to the priority table. The clock source of highest priority is the trace source. The priority table can be configured manually. Figure A-13 shows the clock configuration and the priority table when SSM is disabled.
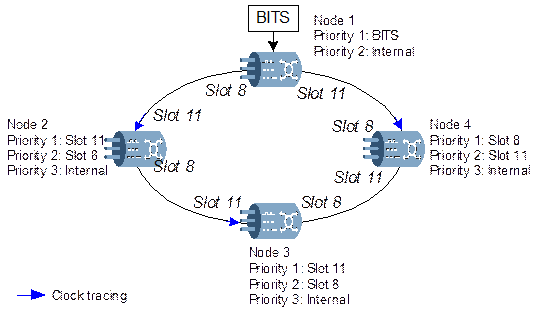
Figure A-13 Networking of clock with disabled SSM
If there is fiber break in the loop, the clock will be traced mutually, as shown in Figure A-14:
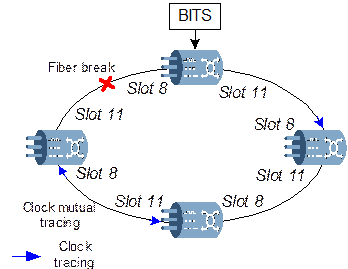
Figure A-14 Clock mutual tracing caused by fiber break
If the SSM function is not enabled, it is not recommended to configure the east and west clocks of an NE into the clock source priority table at the same time.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.