2.2.4 Typical Example of ECC Fault (I)
1. Networking
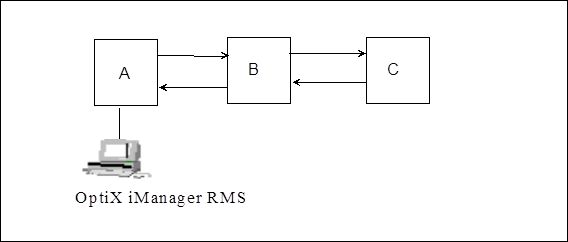
Figure 2-2 Example of networking
A certain office employs OptiX BWS 320G chain networking mode, in which, NM is set in station A, stations A and C are configured with SC1 boards, and station B is configured with SC2 board.
2. Fault descriptions and solution
Station A can not log in to stations B and C normally, but the service is normal. Since the sensitivities of SC1 and SC2 boards are up to about -50dBm, generally, it is not the problem of optical fiber that causes excessive attenuation of optical signal; it suggests that the SCC unit or SC2 board of station B is faulty. Unplug the SCC unit of station B to enable ECC to get through from stations A to C. NM of station A can be log in to station C, indicating that SC2 board is in normal service. Plug the SCC unit of station B again, and normal service of ECC is resumed.
3. Experience and summary
When processing ECC fault, directly resetting the SCC unit of the faulty station is temporary an effective method for troubleshooting.
2.2.5 Typical Example of ECC Fault (II)
1. Networking
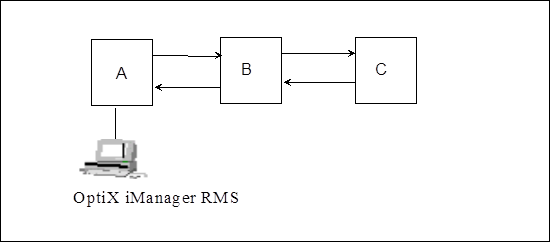
Figure 2-3 Example of networking
A certain office employs OptiX BWS 320G chain networking mode, in which, NM is set in station A, stations A and C are configured with SC1 boards, and station B is configured with SC2 board.
2. Fault description
After the SCC unit of station B is replaced because of fault, it is found that stations A and B can be logged in normally, but the NEs of station C can not.
3. Fault analysis and localization
1) Before the replacement of the SCC unit of station B, all NEs can be logged in from NM terminal; this indicates that there is no problem at NM terminal.
2) After the replacement of the SCC unit of station B, station C can not be logged in. The possible causes are as follows:
There are faults in the SC2 board of station B or the SCC unit, SC1 board of station C, which causes station C not to be logged in.
The ID of SCC unit in station B is not reset, and the ID conflicts with that of station C.
4. Procedures for troubleshooting
1) After the SCC unit of station C is reset, station C can still not be logged in.
2) Check the ID of the SCC unit in station B, it is found that this ID is the same as that in station C.
3) After the ID of the SCC unit in station B is set to that of the original SCC unit, all stations can be logged in normally.
5. Experience and summary
When replacing standby SCC unit, be sure to reset the ID toggle switch to keep its ID consistent with that of the replaced SCC unit, so as to avoid conflicting with the existing ID of NE.
2.3 Orderwire Problem
The orderwire phone of OptiX BWS 320G system is processed by OHP (overhead processing unit). Orderwire byte employs E1 and E2 bytes of monitoring channel, which is extracted from OSC signal by SC1 and SC2 boards and passed to OHP for processing.
2.3.1 Common Causes
(1) External factors -- such as power failure, broken optical fiber and so on.
(2) Wrong setting of telephone set .
(3) Wrong OHP configuration data.
(4) Board faults -- such as SC1, SC2 and OHP.
2.3.2 Common Methods
(1) Alarm and performance analyzing method.
(2) Resetting board.
(3) Substitution method.
2.3.3 Procedures
The problem of orderwire is relatively simple. Check these items in following procedures:
Step 1: first check the optical path.
When optical path is blocked, the orderwire phone can not get through certainly. However, if the fault of optical path affects orderwire, a large amount of alarms and abnormal performance events will be simultaneously generated on the main channel, meanwhile service can not be in normal operation.
Step 2: check the settings of telephone sets of both parties. Most of orderwire problems are caused by incorrect settings of telephone sets.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.