

|
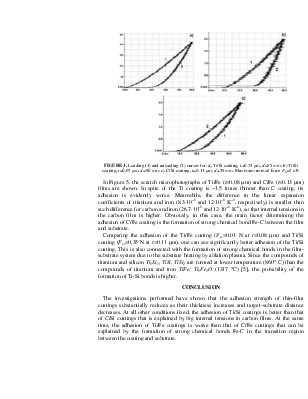
nfluence of Deposition Conditions on Characteristics of Thin-Film Coatings Obtained Using High-Power Ion Beams Vasily K. Struts, Vasily M. Matvienko, Alexandr I. Ryabchikov, Anatoli V. Petrov, Anatoli S. Shlapakovski Nuclear Physics Institute at Tomsk Polytechnic University, 2a Lenin av., Tomsk 634050, Russia Abstract. The films of titanium and carbon deposited onto silicon and a-Fe substrates using high-power ion beams were investigated. The adhesion strength and plasticity of coatings obtained at different deposition conditions have been studied. It has been found that the adhesion strength increases with increasing distance between the substrate and ablated target and with decreasing film thickness determined by a number of accelerator shots. Characteristics of different coatings are compared. INTRODUCTION Thin film deposition from ablation plasma formed under a pulsed high-power ion beam (HPIB) impinging on a target is one of progressive methods for coating details and units of various functions. Structure-phase and mechanical characteristics of such coatings are determined by deposition conditions: HPIB current density, number of pulses, substrate temperature, etc. [1, 2]. An important factor is the distance between the target and substrate. With its variation, the degree of ablation plasma cooling on the way to the substrate changes as well as the film thickness deposited per one HPIB pulse. For smaller temperature difference between the hot plasma and cold substrate, the difference between the linear expansion coefficients of the film and substrate produces a smaller effect of occurrence of internal tensions in the deposited film [3]. Also, the plasma temperature influences on the formation of chemical bonds in the film-substrate system [4]. As a result, the conditions of crystallization of a deposited material are changed. In this work, the results of experimental studies on the adhesion of titanium and carbon films to silicon and ferrous substrates and on their plasticity are presented depending on the target-substrate distance for films of different thickness. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE The HPIB of (70 % H+, 30 % C+) composition was produced from the diode of focusing geometry installed at the accelerator «Temp-2». The accelerated ions energy was 350 keV, the ion current density ranged from 20 to 250 A/cm2 corresponding to the beam energy density of 0.4–5.3 J/cm2 at the pulse duration of 60 ns. The scheme of coatings deposition is presented in Figure 1. The target was positioned in the beam focus at the angle of 45° to the axis. The target-substrate distances were 55, 75, 90, and 190 mm. The substrates were positioned parallel to the target surface. The thickness of films was measured by Linnik interferometer, the adhesion was estimated using the CSEM scratch tester from the value of the critical indentation load, at which a film begins to flake away from the substrate, and from the acoustic emission signal. The plasticity was determined from loading-unloading curves obtained by the CSEM nanohardness meter. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Measurements have shown that the adhesion depends on the thickness of deposited film, which is determined by the number of HPIB pulses at all other deposition conditions fixed. In Figure 2, the value of the critical indentation load Fcr is plotted versus film thickness for the Ti/Si films deposited at the target-substrate distance d=90 mm. It is seen that the adhesion reduces as the film thickness increases; for films thicker than 0.25–0.3 mm, this reduction is not significant, but for thinner films, it is very substantial. For the film thickness t£0.06 mm, the film exfoliation does not take place (in the shown range of the indentation load). One can suppose that internal tensions in the film grow with increasing number of HPIB pulses, so that the adhesion strength decreases [3]. In Table I, the values of Fcr are presented for the Ti/Si coatings of about the same thickness t»0.1 mm obtained at different target-substrate distances by different number of accelerator shots. As the distance d increases, the adhesion improves substantially; at d=190 mm, the film exfoliation was not observed. Table 1. Critical indentation load Fcr for films obtained at different target-substrate distances d |
|
d, mm |
55 |
75 |
90 |
190 |
|
Fcr, N |
0,13 |
0,38 |
0,47 |
>0,5 |
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.