
EVOLUTION OF A NONDETERMINISTIC SELF-OSCILLATION MODE IN A PULSE-PHASE CONTROL SYSTEM WITH INDUCTION MOTOR
Tsukanov V.G., Melikhov A.YU.
Department of Design and Technology of Electronic and Computer Systems,
Orel State Technical University
Naugorskoye Shosse 29, Orel, 302020, Russia
Tel: 7 4862 419879, Fax: 7 4862 416684, E-mail: science-orel@mail.ru
Abstract: Simulation principles of thyristor voltage regulator – induction motor system are represented in this paper. Moreover, causes of the self-oscillation processes in the steady-state conditions of the IM are analyzed here.
INTRODUCTION
One of the first impulse asynchronous electric drive development stages is creation of the system with a pulse-phase control (PPCS) [1]. Thyristor voltage regulator (TVR) represents a power unit with PPCS. Nowadays such control systems are used in soft starters generally [2].
Inspite of the fact that the implementation of the systems with TVR and IM is rather simple, the mathematical description and simulation of such devices bring fundamental complications. This is caused by some peculiarities of PPCS-TVR-IM which will be described in this article.
PROBLEM STATEMENT
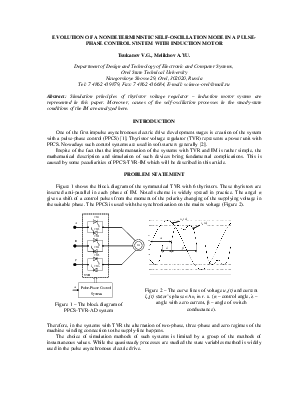
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the symmetrical TVR with 6 thyristors. These thyristors are inserted anti-parallel in each phase of IM. Noted scheme is widely spread in practice. The angel α gives a shift of a control pulses from the moment of the polarity changing of the supplying voltage in the suitable phase. The PPCS is used with the synchronization on the mains voltage (Figure 2).
|
|
Therefore, in the systems with TVR the alternation of two-phase, three-phase and zero regimes of the machine winding connection to the supply-line happens.
The choice of simulation methods of such systems is limited by a group of the methods of instantaneous values. While the quasisteady processes are studied the state variables method is widely used in the pulse asynchronous electric drive.
Nowadays, the electric drive with TVR is chiefly used in soft start systems. That’s why, the behaviors of such systems have the greatest interest during the whole transient from the moment of the switching on till the first several periods of the nominal regime.
Consequently, simulation of such system demands to use general approach rather than the state variables method. Such approach presupposes the compilation of the differential equation system for each interval of structure repetition according Cauchy and the following numerical integration of these systems with the coupling of decisions at the commutation moments.
SIMULATION OF THE TVR-IM SYSTEM WITH PULSE-PHASE CONTROL
The great majority of Russian and foreign publications dealing with unsymmetrical regimes are devoted to the analysis of a steady-state processes. The transient in the case of the unsymmetrical connection of IM can be viewed just with the help of compilation of the differential equations system for such a regime.
Let’s put down the equations for stator and rotor circuits of the three-phase IM for symmetrical regime:
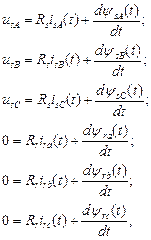 (1)
(1)
wherе Rs (Rr) are resistance of stator (rotor) windings;
usA, usB, usC are mains voltages;
isA(t), isB(t), isC(t) [ira(t), irb(t), irc(t)] are instantaneous values of stator (rotor) currents ;
![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() [
[![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ] are instantaneous values of stator (rotor) flux-linkages;
] are instantaneous values of stator (rotor) flux-linkages;
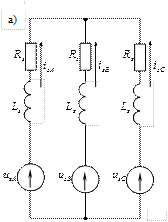
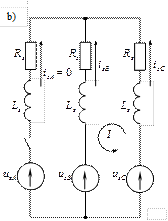
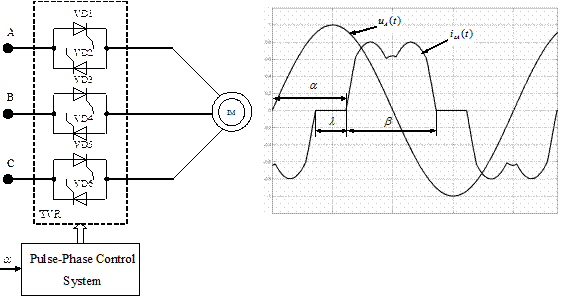
Figure 3 – Scheme of stator circuits of three-phase IM (а - symmetrical regime; b - unsymmetrical regime «BC»)
Let’s make up the equations for unsymmetrical regime «BC» (with the switching off of the phase «А», Figure 3.b). Due to the Kirchhoff's two laws (with tracing the boundary «I» in anticlockwise direction):
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
![]() (4)
(4)
Let’s put the equation (3) into equation (4), we will get the following:
![]() (5)
(5)
Building of the «ВС» regime complete equation system demands to add three equations of the rotor winding voltage balance to the equation (5). These equations don’t change their shape and are equal to the equations of the symmetrical regime (1). Besides, it is necessary to transform the equations of stator and rotor flux-linkages regarding to the conditions (2) and (3).
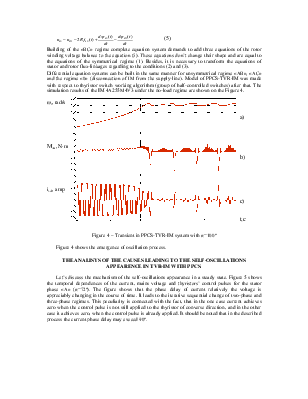
Differential equation systems can be built in the same manner for unsymmetrical regime «АВ», «АС» and the regime «0» (disconnection of IM from the supply-line). Model of PPCS-TVR-IM was made with respect to thyristor switch working algorithm (group of half-controlled switches) after that. The simulation results of the IM 4А255М4У3 under the no-load regime are shown on the Figure 4.
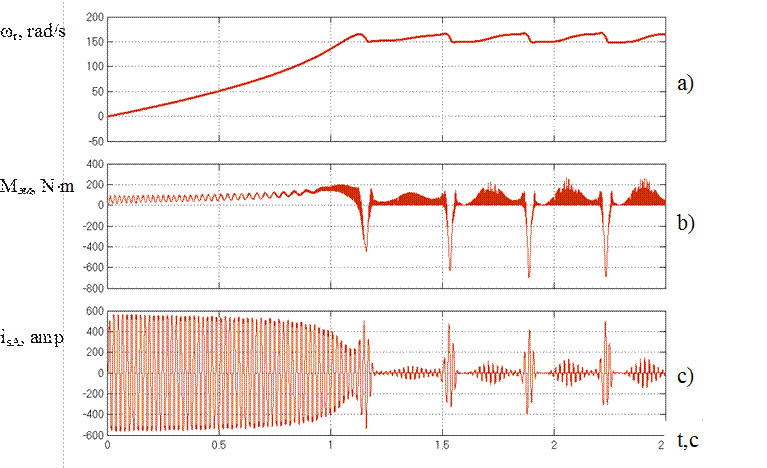
Figure 4 – Transient in PPCS-TVR-IM system with α=100º
Figure 4 shows the emergence of oscillation process.
THE ANALISYS OF THE CAUSES LEADING TO THE SELF-OSCILLATIONS APPEARENCE IN TVR-IM WITH PPCS.
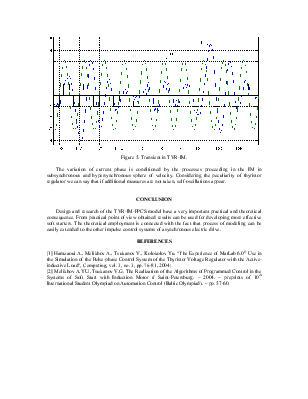
Let’s discuss the mechanism of the self-oscillations appearance in a steady state. Figure 5 shows the temporal dependences of the current, mains voltage and thyristors’ control pulses for the stator phase «А» (α=72º). The figure shows that the phase delay of current relatively the voltage is appreciably changing in the course of time. It leads to the iterative sequential change of two-phase and three-phase regimes. This peculiarity is connected with the fact, that in the one case current achieves zero when the control pulse is not still applied to the thyristor of converse direction, and in the other case it achieves zero, when the control pulse is already applied. It should be noted that in the described process the current phase delay may exceed 90º.
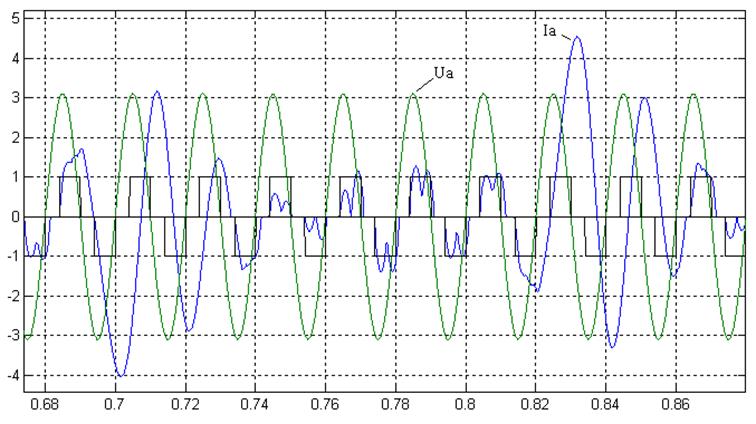
Figure 5. Transient in TVR-IM.
The variation of current phase is conditioned by the processes proceeding in the IM in subsynchronous and hypersynchronous sphere of velocity. Considering the peculiarity of thyristor regulator we can say that if additional measures are not taken, self-oscillations appear.
CONCLUSION
Design and research of the TVR-IM-PPCS model have a very important practical and theoretical consequence. From practical point of view obtained results can be used for developing more effective soft starters. The theoretical employment is connected with the fact that process of modeling can be easily extended to the other impulse control systems of asynchronous electric drive.
REFERENCES
[1] Hamzaoui A., Melikhov A., Tsukanov V., Kolokolov Yu. “The Experience of MatLab 6.0® Use in the Simulation of the Pulse-phase Control System of the Thyristor Voltage Regulator with the Active-inductive Load”, Computing, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 76-81, 2004;
[2] Melikhov A.YU., Tsukanov V.G. The Realization of the Algorithms of Programmed Control in the Systems of Soft Start with Induction Motor // Saint-Petersburg. – 2004. – preprints of 10th International Student Olympiad on Automation Control (Baltic Olympiad). – pp. 57-60.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.