Contents
5 ATM Service Networking 5-1
5.1 Transparent Transmission 5-1
5.2 Multicast 5-4
5.3 Statistical Multiplexing 5-6
5.4 VP-Ring 5-11
Figures
Figure 5-1 Transparent transmission of ATM service 5-2
Figure 5-2 Multicast of ATM service 5-4
Figure 5-3 Statistical multiplexing of ATM services 5-7
Figure 5-4 Typical configuration of NE1 5-9
Figure 5-5 Typical configuration of NE4 5-10
Figure 5-6 Realization of VP-Ring 5-11
Tables
Table 5-1 ATM service requirements of each NE 5-6
This chapter illustrates the networking planning of ATM services and protection through the examples of a variety of ATM services. It includes:
n Transparent transmission
n Multicast
n Statistical multiplexing
n VP-Ring
One of the basic functions of the MSTP equipment is point-to-point transparent transmission of ATM service. The function has the following features:
n Occupy the bandwidth of the SDH equipment exclusively, thus the bandwidth utilization is low.
n Realize protection at SDH layer through the protection switching mechanism of the SDH equipment, achieving high reliability.
Two ATM switches in city 1 and city 2 respectively need to communicate with each other over a 100 Mbit/s bandwidth. The ATM switch provides 155 Mbit/s optical interface and constant bit rate (CBR) services.
The service to exchange needs protection.
The OptiX OSN 3500 is applicable to the transmission of ATM services as required. Figure 5-1 shows the networking diagram.
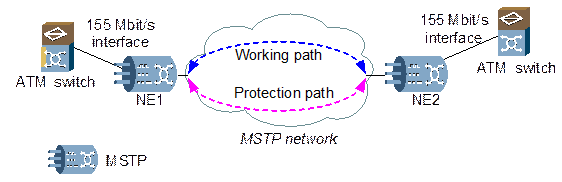
Figure 5-1 Transparent transmission of ATM service
The OptiX OSN 3500 is adopted in city 1 and city 2, named as NE1 and in NE2. The OptiX OSN 3500 interconnects with the ATM switch through the 155 Mbit/s optical interface.
Configure working path and protection path in the MSTP network to protect the ATM service between NE1 and NE2. In addition, configure the ATM service to pass through the SDH NEs that the working path and the protection path pass by.
|
Implementation |
Point-to-point transparent transmission |
|
|
Hardware configuration |
Configure an ADQ1 board in NE1 and NE2 respectively to access the 155 Mbit/s ATM service from the ATM switch. For slots of the ADQ1 board, refer to “Appendix A Network Configuration Requirements”. |
|
|
Traffic control |
NE1 |
NE2 |
|
Service type: CBR |
Service type: CBR |
|
|
Peak cell rate (PCR): 235850 cells/s |
PCR: 235850 cells/s |
|
|
Cell delay variation tolerance (CDVT): 500ms |
CDVT: 500ms |
|
|
Service route |
NE1 |
NE2 |
|
ATM external port 1 ïð ATM internal port 1 ïð VC-4 (working path) |
VC-4 (working path) ïð ATM internal port 1 ïð ATM external port 1 |
|
|
Note: The ATM external port of ADQ1 is the external optical port used to access ATM services, while the ATM internal port refers to the logical port used to connect the ATM processing module and the SDH cross-connect module. |
||
|
Protection route |
NE1 |
NE2 |
|
ATM external port 1 ïð ATM internal port 2 ïð VC-4 (protection path) |
VC-4 (protection path) ïð ATM internal port 2 ïð ATM external port 1 |
|
|
The service can be protected by the protection scheme of SDH equipment networking. The VPI and VCI of the working path may be the same as that of the protection path. |
||
The 155 Mbit/s optical interface feature of ATM is the same as STM-1 of SDH. If the MSTP equipment is not necessary for processing ATM services, SDH line boards (such as SLQ1) can be used, instead of ATM boards.
Multicast is a kind of point-to-multipoint transmission (such as broadcast), where the central station transmits signals to every end office. In broadcast, a message is transmitted from a subscriber to all subscribers located in the network. It is usually unidirectional and is applicable to transmit TV and broadcasting programs.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.