1. Classification Principle of SLA Service
The SLA service can be classified into multiple levels in terms of protection (service with high level, service with medium level, re-routed service, non-protected service and extra service, and so on). Charges for services at different levels are different, thus demands of different users can be satisfied flexibly. Principle for classifying services is as follows:
n Service priority: Provided with 1+1 protection or alike, with the switching time being 0–20 ms.
n Service priority: Provided with M:N protection and alike (for example, two-fiber MSP), with the switching time being 0–50 ms.
n Re-routed service: Real-time re-calculates the path, with the switching time from 100 ms to several seconds.
n Non-protected service: Provided with no protection at fault occurrence.
n Extra service: Pre-empted by services with higher priorities when the network resource is insufficient.
2. SLA-Based Protection at Different Service Levels
With the SLA service provided, the OptiX OSN 9500 enables the operators to win more customers in a differential market with better service and lower cost.
Table 4-1 Differential protection for service at different levels
|
Service level |
Protection level |
Service quality |
|
Diamond |
High level protection |
The quality of services listed in the left column grows higher from bottom to top. |
|
Gold |
Medium level protection |
|
|
Silver |
Re-routing protection |
|
|
Copper |
Not protected |
|
|
Iron |
Redundant |
Service of diamond level is to meet demands of users such as banks, securities, important government offices, and so on. Service of gold level is to satisfy the demands for speech, multimedia and video. Service of silver level is applicable to common data service transmission. Services of copper and iron levels are suitable for applications such as family network access.
As shown in Figure 4-4, for the service of diamond level, a path ring (dotted line) is defined first for an end-to-end protected service (dual-fed and selective received) of one pair of access equipments. The figure shows the unidirectional service. The bidirectional service is similar. In normal conditions, the receiving end receives service from the upper dot line side. When a failure occurs to the link or node, the service will be switched to the lower dot line side for receiving.
You can also select not pre-defining the path ring, but calculating two end-to-end paths (which are not intersecting) from the edge service access node of the optical network. In such a case, the service is dual fed at the head end and selectively received at the tail end, thus guaranteeing the service of diamond level.
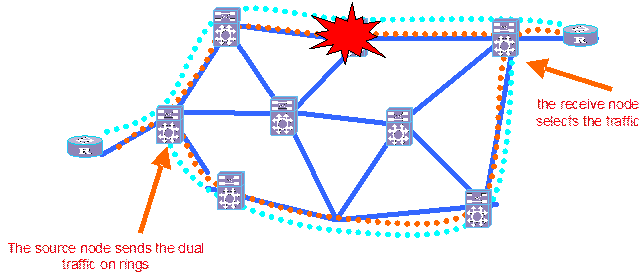
Figure 4-4 Networking protection for service of diamond level
For service of gold level, the logical virtual MS ring must be pre-defined. As shown in Figure 4-5, the bandwidth of Ring 1, Ring 2 and virtual ring are specified as the user demands. They can be part of the maximum bandwidth of the optical fiber. Half timeslots of the MS ring are used to protect another half timeslots. To provide service with medium level with M: N protection, the edge service access node of the optical network calculates which the respective link of the service trail belongs to. By doing so, a rapid MSP switching can be guaranteed at any link or node failure on the service path. As shown in Figure 4-5, all links of the end-to-end service path belong to either Ring 1 or Ring 2. If one node fails, as shown in the figure, service on Ring 2 can be switched to the protection path of the ring rapidly.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.