n Dynamic bandwidth allocation significantly improves the bandwidth availability.
n Services can be turned up rapidly and flexibly according to the signaling request.
n End-to-end (ring-crossing) services are provided with protection.
n Auto-balance and optimization of the network load.
n With SLA service provided, differential services are available.
n Network management is simplified, and the unified NM over different networks is realized finally.
4.2 Principle of Intelligent Optical Network
As requirements are promoted by data service for bandwidth and service quality of the optical network, the optical network is urged to develop into one with flexible and intelligent control and management capability instead of the traditional one with only the originally fixed bandwidth provided.
The intelligent optical network system is put forward in response to such requirements. It may classify the services and intelligently configure them according to the traffic in the network. When a fault occurs in the network, the network is endowed with powerful survivability. As a result, the optical transmission network is provided with real-time management capability over the configurable bandwidth and the dynamic end-to-end service connection.
What makes the intelligent optical network distinctive is the control plane. The control plane works with the switching capability controlled by signaling to make the management over connection configuration possible. So, the signaling protocol of the control plane is of vital importance to the intelligent optical network.
As shown in Figure 4-1, three interface protocols are involved in the intelligent optical network: User network interface (UNI), internal network to network interface (I-NNI) and external network to network interface (E-NNI).
UNI defines the protocol of the service control interface between the user device and the intelligent optical network equipment.
E-NNI defines the interworking protocol of the optical network equipments of different venders, with GMPLS as the main body of its signaling protocol.
I-NNI is the internal protocol customized by the manufacturers. To make a smooth transition to the ultimate peer-to-peer model, protocol signaling such as open shortest path first (OSPF) should be followed during the customization, thus guaranteeing convenient upgrade and interconnection in the future.
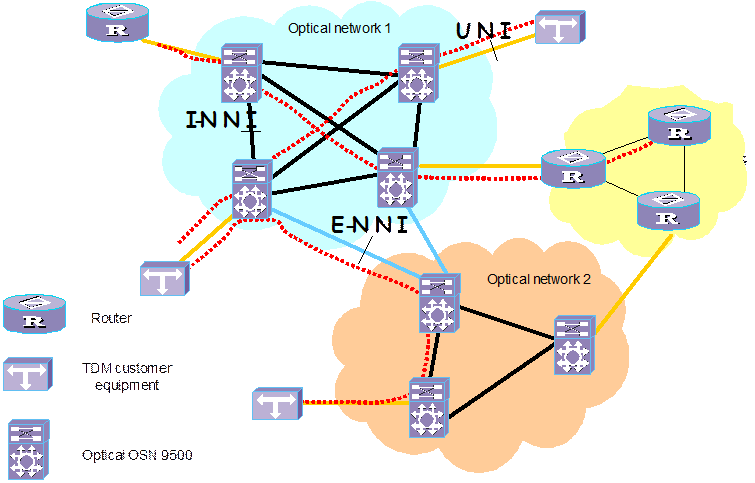
Figure 4-1 Principle model of intelligent optical network
4.2.2 Architectural Model
As shown in Figure 4-2, the intelligent optical network includes two layers: the control plane and the service plane (or transmission plane).
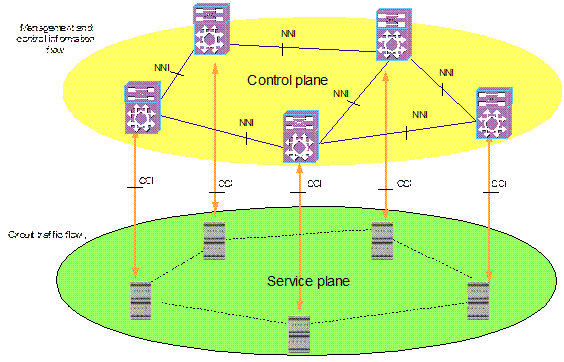
Figure 4-2 Control and service planes of intelligent optical network
The control plane collects and disperses the network topology information of the intelligent optical network control plane. It provides the control plane route through the SPF algorithm. It is mainly the management and control information flow running on this plane.
The service plane is mainly the circuit traffic flow running on this plane.
4.2.3 Application Technologies
1. OSPF
OSPF is a dynamic route protocol based on link status and SPF algorithm. It learns the network (in AREA) topology information by exchanging link status between neighbors and works out all routes of destinations in the AREA by SPF algorithm.
The OSPF route module collects the network topology information, including that of the control layer and the service topology information for calculating the constrained service route. It also collects the network protection information and calculates routes based on the collected topology information.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.