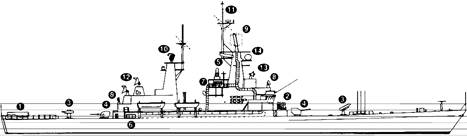
Missiles: SSM: 8 GDC Tomahawk (2 quad) launchers (1); combination of (a) land attack; TAINS to 2 500 km ( 1 400 nm) at 0.7 Mach; altitude 15-100 m (49.2-328.1 ft): warhead nuclear 200 kt or various conventional HE.
(b) anti-ship; inertial guidance; active radar and anti-radiation homing to 460 km (250 nm) at 0.7 Mach; warhead 454 kg. 8 McDonnell Douglas Harpoon (2 quad) launchers (2); active radar homing to 130 km (70 nm) at 0.9 Mach; warhead 227 kg (84A)or258kg (84B/C).
SAM: GDC Pomona Standard MR-SM2; semi-active radar homing to 73 km (40 nm).
A/S: Honeywell ASROC: inertial flight to 1.6-10 km (1 5,5 nm): payload 1 kt nuclear depth bomb or Mk 46 torpedo. SAM and A/S missiles are fired from 2 twin Mk 26 launchers supplied by a total of 68 weapons (3).
Guns: 2 FMC 5 in (127 mm) Mk 45 (4); 65° elevation; 20 rounds/minute to 23 km (12.6 nm) anti-surface; 1 5 km (8.2 nm) anti-aircraft; weight of shell 32 kg.
2 General Electric/General Dynamics 20 mm Vulcan Phalanx 6-barrelled Mk 15 (5); 3 000 rounds/minute combined to 1 .5 kg. 2—40 mm IVIk 11 saluting guns.
Torpedoes: 6—324 mm Mk 32 (2 triple) tubes (6) Honeywell Mk 46; anti-submarine; active/passive homing to 11 km (6 nm) at 40 knots; warhead 44 kg
Countermeasures: Decoys: 4 Tracer MBA SRBOC 6-barrelled fixed Mk 36 (7); IR flares and Chaff to 4 km (2.2 nm). T Mk 6 Fanfare; torpedo decoy system.
ESM/ECM: SLQ 32V (3); combined radar warning and jammers.
Fire control: 1 Mk 74 missile control director. 1 digital Mk 116 ASW FCS. 1 IVIk 86 WCS for forward missile channel and gun fire. NTDS. OE-82 satellite communications antenna (8); SSR-1 receiver; 4 WSC-3 transceivers
Radars: Air search: ITT SPS 48D/E (9); 3D; E/F band: range 402 km (220 nm). Lockheed SPS40B (10): E/F band; range 320 km (175 nm).
Surface search: ISC Cardion SPS 55 (11); I/J band.
Navigation: Marconi LN 66 (CGN 39, 41 ); I/J band.
Firecontrol:Two SPG51 (12);G/I band.
SPG 60D (13); I/J band, SPQ 9A (14); I/J band
Tacan: URN 20.
Part of the New Threat Upgrade are significant improvements to SPS 48 radar: SPS 48E radar modification provides higher elevation angle coverage, increased average power output and provides frequency and pattern flexibility to defeat jamming while detecting targets through heavy clutter. Also included is the addition of the SYS 2 integrated automatic detection and tracking system that integrates outputs of SPS 48 and 40 air search radars to provide a correlated track file.
VIRGINIA
(Scale 1 : 1 800)
VIRGINIA
Sonars: EDO/GE SQS 53A; bow-mounted; active search and attack; medium frequency. Based on SQS 26 but with digital computers
Programmes: Virginia was authorised in FY 1970, Texas in FY 1971, Mississippi in FY 1972, and Arkansas in FY 1975, Originally classified as guided missile frigates (DLGN); subsequently reclassified as guided missile cruisers (CGN) on 30 June 1975.
Modernisation: Standard SM-1 MR replaced bySM-2MR using Block II missiles to counter current and protected anti-ship cruise missile threats at extended ranges in the presence of severe enemy electronic countermeasures. Production systems were deployed in all guided-missile cruisers and in "DDG 993" class destroyers in FY 1988. The initial phase of fleet introduction of SM-2 in a Tartar ship was completed in May 1986 in Virginia. Tomahawk fitted in all of the class at the expense of the helicopter capability. Structure: The principal differences between the "Virginia" and “California" classes are the provision of improvements to anti-air warfare capability, electronic warfare equipment, and anti-submarine fire control system. The deletion of the separate ASROCMk16 launcher permitted the "Virginia" class to be 1 1 ft shorter.
A hangar for helicopters was installed beneath the fantail flight-deck with a telescoping hatch cover and an electromechanical elevator provided to transport helicopters between the main deck and hangar; the installation of Tomahawk right aft meant the removal of helicopter facilities.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.