Carrier/channel selection can be implemented in the digital domain (DUC/DDC). The single channel ADC/DAC does not receive/transmit a low frequency baseband signal, but an intermediate frequency (IF). The IF is defined by the frequency of the digital sine and cosine generator, which is a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO). The IF signal is up/down converted to/from RF through one analog mixing stage, reducing the RF BOM. The IF frequency is usually in the 70 MHz to 200 MHz range. Benefits · No LO/carrier self-mixing at IF, perfect gain/phase matching, no offset. · High IF relaxes RF front-end image rejection filter requirement. · Reduces RF BOM (Bill of Materials). Tradeoffs · High IF requires a wideband data converter, but ADC/DAC performance at such a high IF range limits the performance of such an architecture. · Carrier/channel selection can be implemented in the digital domain (DUC/DDC) but requires a high speed ADC/DAC. |
Wireless Infrastructure: Direct Conversion RX/TX
|
Wireless Infrastructure: Direct Conversion RX/TX Solutions from Texas Instruments |
Wireless Infrastructure: WCDMA & CDMA2000 4/8-Carrier, Receive Diversity RX/TX
|
Wireless Infrastructure: WCDMA & CDMA2000 4/8-Carrier, Receive Diversity RX/TX Solutions from Texas Instruments |
Wireless Infrastructure: TD-SCDMA RX/TX
|
|

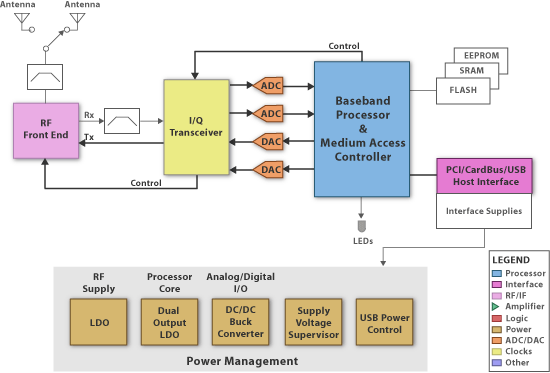
WLAN Card
The WLAN Card is used with a personal computer to access a Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN), which can extend or replace traditional wired computer networks by transmitting and receiving data radio waves using Spread-Spectrum Technology (SST). There are four main standards for WLANs: 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. The last 3 standards operate in the same environment without causing interference with each other. The 802.11b is the dominant standard with 11-Mbps rates in the 2.4HGz band. The 802.11a is capable of reaching 54-Mbps rates in the 5GHz band. The 802.11g standard also has 54-Mbps but is compatible with 802.11b. The 802.11b technology implements the Digital Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) modulation. The 802.11a/g implements the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. Core Subsystem include:
· RF/IF Front End - filters/amplifies RF signal and performs RF-to-IF conversion to generate I and Q data for ADC and DAC.
· Baseband Processor of Physical Layer (PHY) - modulates and demodulates I and Q data and performs carrier sensing, transmission and receiving frames.
· Medium Access Controller (MAC) - controls the communication (access) between client and applications.
· Power Conversion - receives power supply via the host interface.
Wireless Infrastructure: Hi-Perf WiMAX 802.16, 2.5-3.5GHz BTS RX/TX
|
Wireless Infrastructure: Hi-Perf WiMAX 802.16, 2.5-3.5 GHz BTS RX/TX In Hi-Perf WiMAX 802.16, 2.5-3.5 GHz BTS RX/TX, Baseband data is interpolated and filtered in the DUC. The DUC presents parallel IQ data to the dual DAC. The DAC provides high speed data conversion of the IQ data. In addition, phase, gain and offset correction of the IQ imbalance are possible using the full featured DAC capabilities. With a complex baseband input, an interpolating DAC can be used to increase the effective data rate through interpolation. The process of complex mixing to translate the signal frequency from baseband to an IF frequency produces sideband and LO feed through, at the IQ modulator output, that falls outside the signal band of interest. The IQ-modulator is capable of performing at frequencies from 0.4-4 GHz, and is thereby suitable to meet the popular WiMAX frequency bands. The CDC/M provides clock recovery, jitter cleaning functions, and is used to generate all the necessary system clocks. SerDes devices provide the parallel-to-serial conversion to implement a high speed interconnect between Baseband and RF cards. The receive chain down converts RF to IF through one analog mixing |
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.