Table 5-1 shows the maximum number of signals with different rates that can be accessed at a single subrack.
Table 5-1 Maximum number of signals that can be accessed at a single subrack
|
Rate |
Cross-connect capacity |
Max. number |
|
STM-64 |
720 G |
40 |
|
400 G |
40 |
|
|
STM-16 |
720 G |
288 |
|
400 G |
160 |
|
|
STM-4 |
720 G |
640 |
|
400 G |
448 |
|
|
STM-1(O) |
720 G |
640 |
|
400 G |
640 |
|
|
STM-1(E) |
720 G |
640 |
|
400 G |
640 |
Note: the above data are worked out with the maximum cross-connect capacity, slot number, configuration of boards with different rates, and maximum access capacity of each board of the OptiX OSN 9500 taken into overall consideration.
& Note:
The above figure shows the maximum access capacities for signals with different rates when the cross-connect capacity of the system is different. In practical networking, signals at rates of STM-64, STM-16, STM-4 and STM-1 can be mixed in the configuration as desired, if only the total access capacity does not go beyond the maximum cross-connect capacity of the equipment.
Table 5-2 shows the access capacities of respective interface boards on the subrack.
Table 5-2 Access capacities of respective boards
|
Board name |
Full name |
Processing capability |
Access capacity |
|
JL64 |
STM-64 optical interface board |
1 x STM-64 |
10 G |
|
JO16 |
8 x STM-16 optical interface board |
8 x STM-16 |
20 G |
|
JQ16 |
4 x STM-16 optical interface board |
4 x STM-16 |
10 G |
|
JD16 |
2 x STM-16 optical interface board |
2 x STM-16 |
5 G |
|
JL16 |
1 x STM-16 optical interface board |
1 x STM-16 |
2.5 G |
|
JLQ4 |
4 x STM-4 optical interface board |
4 x STM-4 |
2.5 G |
|
JH41 |
16 x STM-4/STM-1 optical interface board |
16 x STM-1, 16 x STM-4 or mixture of multiple STM-1s and STM-4s. |
10 G |
|
JLH1 |
16 x STM-1 optical interface board |
16 x STM-1 |
2.5 G |
|
JLHE |
16 x STM-1 electrical interface board |
16 x STM-1 |
2.5 G |
|
GE06 |
6-port Gigabit Ethernet processing board |
6 x 1000M |
10 G |
|
GXCL |
General Low Order Cross-Connect board |
8064 x 8064 VC-12 |
20 G |
The access capacity supported by each IU slot varies with the configured cross-connect capacity of the equipment. The following is the detailed description.
2. Service Slot Configuration when Configured with the GXCH Board
When the equipment cross-connect capacity is configured as 400 G (that is, configured with the GXCH board), that for each IU slot is shown in Figure 5-1. For example, when a 20 G slot is configured with a 20 G board, the corresponding two 5 G slots can respectively provide an access capacity of only 5 G.
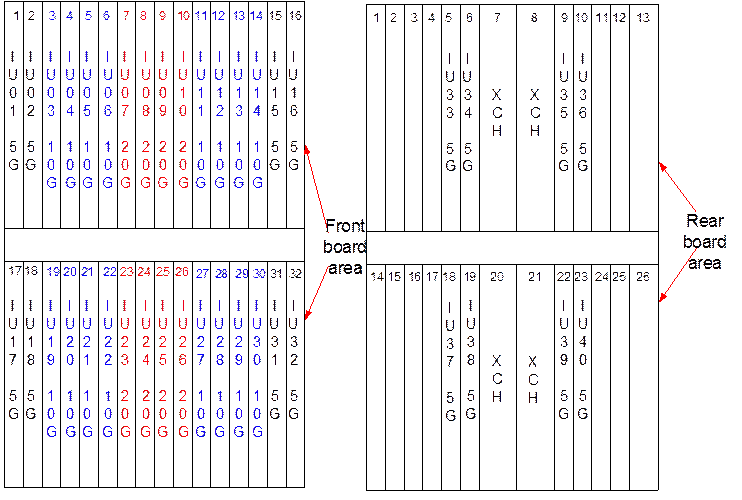
Figure 5-1 Max. access capacity of each IU slot when configured with the GXCH board
If the 20 G slot is only configured with a 10 G board, then the corresponding two 5 G slots can respectively provide an access capacity of 10 G. Table 5-3 shows the relation between 20 G slots and 5 G slots.
Table 5-3 The relation between 20 G slots and 5 G slots
|
20 G Slots |
Corresponding 5 G slots |
|
IU07 |
IU01, IU02 |
|
IU08 |
IU33, IU34 |
|
IU09 |
IU35, IU36 |
|
IU10 |
IU15, IU16 |
|
IU23 |
IU17, IU18 |
|
IU24 |
IU37, IU38 |
|
IU25 |
IU39, IU40 |
|
IU26 |
IU31, IU32 |
Table 5-4 Slots for respective interface boards when configured with the GXCH board
|
Board name |
Silkscreen |
|
JO16/GXCL |
IU07–IU10 and IU23–IU26 |
|
JL64/JQ16/JH41/GE06 |
IU03–IU14 and IU19–IU30 |
|
JD16/JLQ4/JLH1/JLHE |
IU01–IU40 |
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.