144 Total Organizational Excellence
Defining improvement opportunities and prioritizing 145
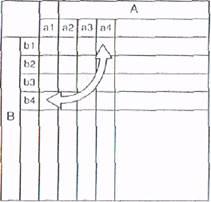
Figure 9.16 L-shaped matrix
in one application, customer demands (the 'whats') arc analysed with respect to substitute quality characteristics (the 'hows') (Figure 9.17). Correlations between the two are categorized as strong, moderate and possible. The customer demands shown on the left of (the matrix arc determined in cooperation with the customer. I his effort requires a kind of a vernal 'p ing-pong' with (he customer to he truly effective ask the customer what he wants, write it down, show it to him and ask him if that is what he meant, then revise and repeat the process as necessary. This should be done in a joint meeting with the customer, if at all possible. It is often of value to use a tree diagram to give structure to this effort.
|
|
|
Figure 9.17 An example of the matrix diagram |
The right side of the chart is often used to compare current performance to competitors' performance, company plan and potential sales points with ref-
|
MFR |
Ash |
Importance |
Current |
Best compolitior |
Plan |
IR |
SP |
ROW |
|
|
No film breaks |
17 |
Д.. 6 |
1 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
о |
6.6 |
|
High rates |
® 23 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
л |
1.3 |
4.6 |
||
|
Low gauge variability |
® 37 |
A 7 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
Л |
1.3 |
о |
7.3 |
![]()
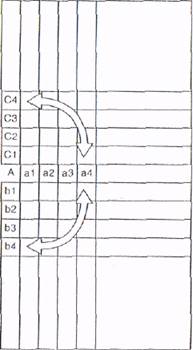
Figure 9.18 T-shaped matrix
erence to the customer demands. Weights are given to these items to obtain a 'relative quality weight'. This can be used to identify the key customer demands. The relative quality weight Is then used with the correlations identified on the matrix to determine the key quality characteristics.
(ii) T-shaped matrix diagram
The T-shaped matrix is nothing more than the combination of two L-shaped matrix diagrams. As can he seen in f'igurc 9.18, it is based on the premise that two separate sets of items arc related to a third set. Therefore, A items are somehow related to both B and С items
F'igurc 9.19 shows one application. In this case, it shows the relationship between a set of courses in a curriculum and two important sets of considerations: who should do the training for each course and which would be the most appropriate functions to attend each of the courses.
It has also been widely used to develop new materials by simultaneously relating different alternative materials to two sets of desirable properties.
There are other matrices that deal with ideas such as product or service function, cost, failure modes, capabilities, etc., and there arc at least 40 different types of matrix diagrams available.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.