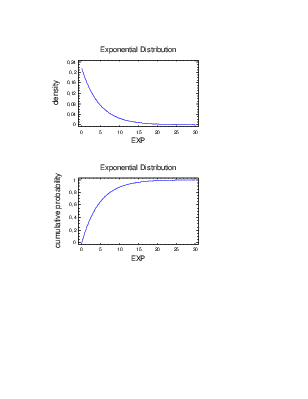
Uncensored Data - EXP
Analysis Summary
Data variable: EXP
100 values ranging from 0,0746175 to 28,8372
Fitted exponential distribution:
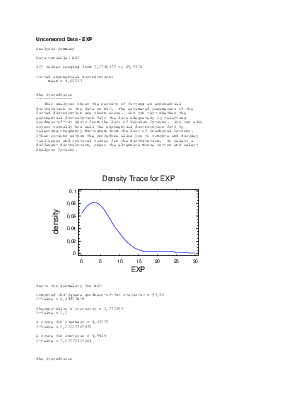
mean = 4,65513
The StatAdvisor
--------------This analysis shows the results of fitting an exponential
distribution to the data on EXP. The estimated parameters of the
fitted distribution are shown above. You can test whether the
exponential distribution fits the data adequately by selecting
Goodness-of-Fit Tests from the list of Tabular Options. You can also
assess visually how well the exponential distribution fits by
selecting Frequency Histogram from the list of Graphical Options.
Other options within the procedure allow you to compute and display
tail areas and critical values for the distribution. To select a
different distribution, press the alternate mouse button and select
Analysis Options.
Tests for Normality for EXP
Computed Chi-Square goodness-of-fit statistic = 83,36
P-Value = 2,19907E-9
Shapiro-Wilks W statistic = 0,770183
P-Value = 0,0
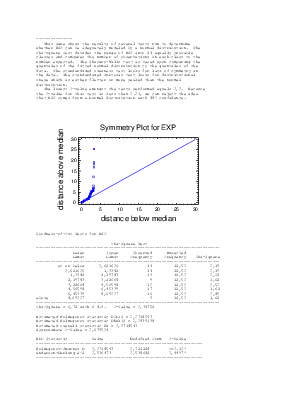
Z score for skewness = 4,63005
P-Value = 0,00000365975
Z score for kurtosis = 4,8914
P-Value = 0,00000100261
The StatAdvisor
--------------This pane shows the results of several tests run to determine
whether EXP can be adequately modeled by a normal distribution. The
chi-square test divides the range of EXP into 24 equally probable
classes and compares the number of observations in each class to the
number expected. The Shapiro-Wilks test is based upon comparing the
quantiles of the fitted normal distribution to the quantiles of the
data. The standardized skewness test looks for lack of symmetry in
the data. The standardized kurtosis test looks for distributional
shape which is either flatter or more peaked than the normal
distribution.
The lowest P-value amongst the tests performed equals 0,0. Because
the P-value for this test is less than 0.01, we can reject the idea
that EXP comes from a normal distribution with 99% confidence.
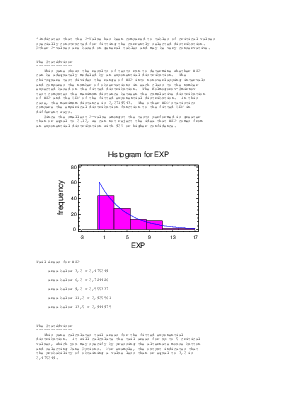
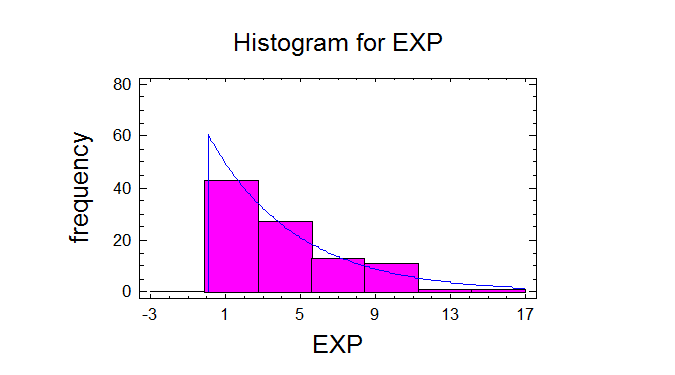
Goodness-of-Fit Tests for EXP
Chi-Square Test
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Lower Upper Observed Expected
Limit Limit Frequency Frequency Chi-Square
---------------------------------------------------------------------------at or below 0,621606 14 12,50 0,18
0,621606 1,3392 14 12,50 0,18
1,3392 2,18793 13 12,50 0,02
2,18793 3,22669 8 12,50 1,62
3,22669 4,56589 10 12,50 0,50
4,56589 6,45338 17 12,50 1,62
6,45338 9,68007 16 12,50 0,98
above 9,68007 8 12,50 1,62
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Chi-Square = 6,72 with 6 d.f. P-Value = 0,34752
Estimated Kolmogorov statistic DPLUS = 0,0719543
Estimated Kolmogorov statistic DMINUS = 0,0438139
Estimated overall statistic DN = 0,0719543
Approximate P-Value = 0,678504
EDF Statistic Value Modified Form P-Value
--------------------------------------------------------------------Kolmogorov-Smirnov D 0,0719543 0,721229 >=0.10*
Anderson-Darling A^2 0,536473 0,539692 0,4487*
--------------------------------------------------------------------*Indicates that the P-Value has been compared to tables of critical values
specially constructed for fitting the currently selected distribution.
Other P-values are based on general tables and may be very conservative.
The StatAdvisor
--------------This pane shows the results of tests run to determine whether EXP
can be adequately modeled by an exponential distribution. The
chi-square test divides the range of EXP into nonoverlapping intervals
and compares the number of observations in each class to the number
expected based on the fitted distribution. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov
test computes the maximum distance between the cumulative distribution
of EXP and the CDF of the fitted exponential distribution. In this
case, the maximum distance is 0,0719543. The other EDF statistics
compare the empirical distribution function to the fitted CDF in
different ways.
Since the smallest P-value amongst the tests performed is greater
than or equal to 0.10, we can not reject the idea that EXP comes from
an exponential distribution with 90% or higher confidence.
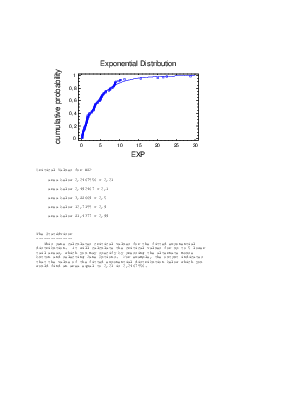
Tail Areas for EXP
area below 3,0 = 0,475049
area below 6,0 = 0,724426
area below 9,0 = 0,855337
area below 11,0 = 0,905861
area below 13,5 = 0,944978
The StatAdvisor
--------------This pane calculates tail areas for the fitted exponential
distribution. It will calculate the tail areas for up to 5 critical
values, which you may specify by pressing the alternate mouse button
and selecting Pane Options. For example, the output indicates that
the probability of obtaining a value less than or equal to 3,0 is
0,475049.
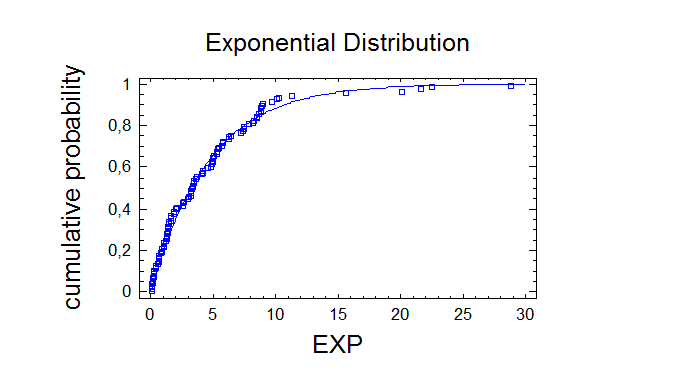
Critical Values for EXP
area below 0,0467856 = 0,01
area below 0,490467 = 0,1
area below 3,22669 = 0,5
area below 10,7188 = 0,9
area below 21,4377 = 0,99
The StatAdvisor
--------------This pane calculates critical values for the fitted exponential
distribution. It will calculate the critical values for up to 5 lower
tail areas, which you may specify by pressing the alternate mouse
button and selecting Pane Options. For example, the output indicates
that the value of the fitted exponential distribution below which you
would find an area equal to 0,01 is 0,0467856.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.