The aim of the modelling is carrying out the processes taking place in two modes switched reluctance machine: the I.C.E. start-up mode and a generator mode.
Designed SRM, using in a starter mode should meet rigid requirements. The following concern to them: overcoming of force of friction of rest I.C.E. and his further dispersal till the speed 180 rpm, rotation with rated speed should proceed during time, sufficient for start serviceable I.C.E. Dispersal up to rated speed whenever possible should occur for very short time interval. This requirement is caused by the high starting stator currents, and consequently also the high allocation of energy on active elements of the converter.
Switching SRM in a generator mode should occur at once after start I.C.E. In all a speeds range of I.C.E. cranked shaft (from 500 rpm and is higher) switched reluctance generator should provide the rated power making of a little some hundreds watt. The power generated by the switched reluctance generators controlled by the voltage feedback control system by the appropriate definition of dwell angle.
The researched model of the starter - generator is shown in fig. 4. It consist of the following blocks: a voltage source (the battery), the voltage converter, the switched reluctance machine, the torque source, the pulses shaper, RLC-load, a current feedback.
The electric part of the switched reluctance machine is represented by a nonlinear model bases on the magnetization characteristic composed of several magnetizing curves and on the torque characteristic computed from the magnetization curves.
The mechanic part is represented by a state-space model based on inertia, moment and viscous friction coefficient. In the specific SRM model, the magnetization characteristic of the motor is provided in a look-up table. The values obtained by calculated by finite-element analysis.
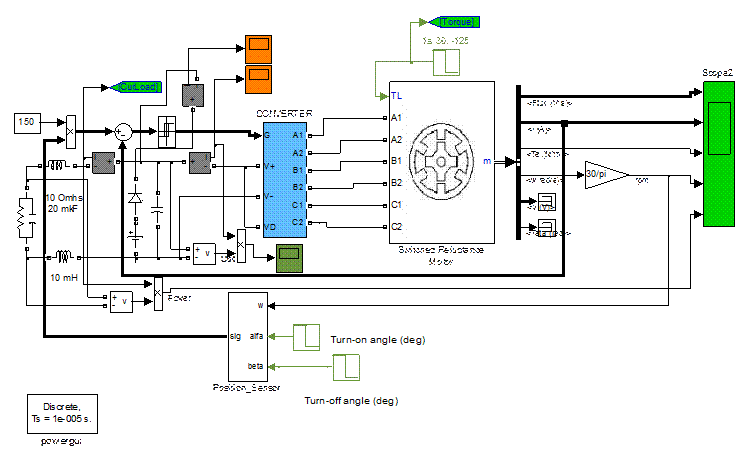
Fig. 4. Researched model
Carry out of the engine starting having set the nominal load moment Tn=30 N×m, rated voltage Udc=12V and restriction of a stator current Ilim=150 A. The rotor inertia is equal to zero for torque ripple supervision. For two converters topology fig. 5 illustrates the following processes: flux linkage, stator current, a torque, rotor speed, a voltage source current.
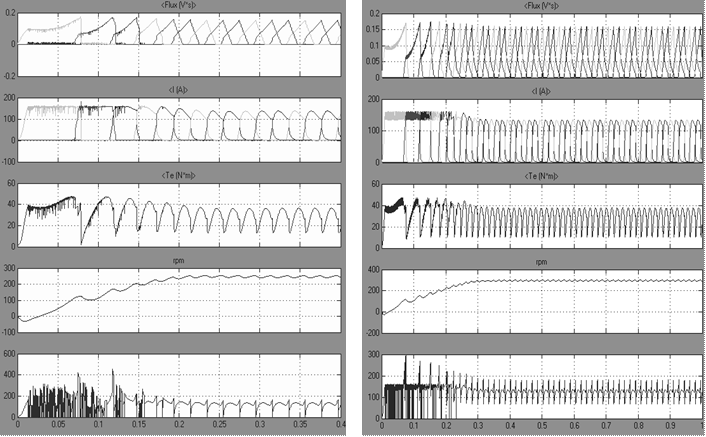
a) b)
Fig. 5. Processes for the converters:
a – classical; b – suppression resistor
Voltage and current regulation at work SRM in a generator mode is necessary. For this purpose the feedback is entered. Load power controlled by the appropriate definition of dwell angle. The feedback structure is submitted on fig. 6.

Fig. 6. Feedback structure
The selector of the minimal control error is used for maintenance of voltage stabilization at value of a load current below set. The chosen control error moves on a PI control law.
The system passes in a current stabilization mode at excess the set value by a current. Such characteristic of a generator control system is necessary at work in a complex with an electric equipment of the automobile.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.