Every connection into the origin server consumes resources independent of the actual data flowing through the connection. As the number of connections increase, this load can become inordinately large and adversely affect the server performance. The edge server greatly mitigates this problem by aggregating connections. The edge multiplexes the connections from a large number of clients on to one connection to the origin server.
Such constraints may prompt the Flash Media Server and network administrators to consider a different deployment strategy. The strategy involves configuring Flash Media Server to redistribute the load on system and bandwidth resources by running some virtual hosts as edge servers and other virtual hosts as origin servers.
Rather than forwarding every request to the origin server and consuming resources for such repetitive tasks, the edge server collects the requests from a large number of clients and aggregates them into one connection to the origin server. All communications between edge and origin servers happen transparently to the users.
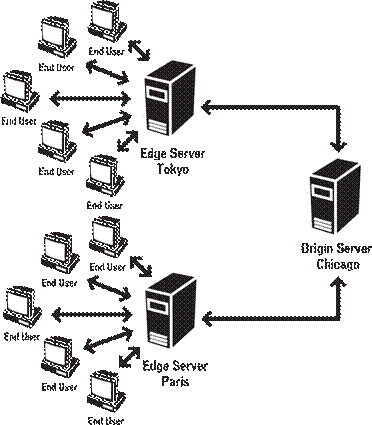
To distribute the demands on network and system resources, administrators can assign the users in a geographical region or functional area of the organization to a specific edge server. For example, one edge server might aggregate and forward requests from users in Tokyo and another might aggregate and forward requests from Paris. The edge servers in Paris and Tokyo gather the requests from their clients and forward them to the origin server located in another secured location, such as Chicago.
Users in these zones always access the origin server through their assigned edge servers. These edge servers receive the responses from the origin server, then distribute them back to the clients (the users’ computers) in their respective zones: Paris or Tokyo. The edge also stores the data received from the origin server in a cache, and makes it available to other clients that connect to this edge server. Recycling the data is one more way that edge servers use resources efficiently. Caching static content reduces the overall load placed on the origin server.
A networked Flash Media Server deployment involves multiple edge servers; these can be deployed individually or in clusters. Edge servers can also be chained, where one edge server collects and aggregates the connection requests from other edge servers and their clients, then transmits the requests to an origin server.
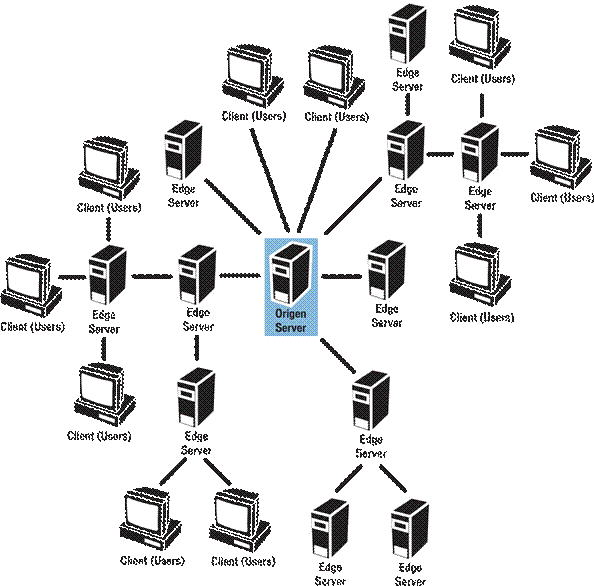
An edge server is designed to intercept the requests for Flash Media Server services from users in a particular zone, collect or aggregate these requests, and transmit them to the origin server. The origin server returns the results to the edge server, which in turn sends the data back to the user’s client computer. The edge server also stores this information in its cache, where other users or clients assigned to the same edge server can access it. In this scenario, fewer requests for services are forwarded to the origin server.
The edge server caches data such as video streams and shared objects. When a user requests data that is found in the edge server’s cache, it returns the data to the requesting client (the user’s computer) without ever calling upon the origin server. This detour is transparent to the user. The edge server is conserving bandwidth by not connecting to the origin server. In this scenario, no demands are placed on the origin server.
Edge servers may be deployed in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) of a corporate network. A
DMZ is an isolated network placed between an organization’s trusted network and the Internet’s untrusted network. In this deployment, the edges function as proxy servers for all Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) traffic that flows through the organization’s network. Deploying edge servers in the DMZ provides one more layer of defense between the user’s Internet connection and the origin server. All traffic that comes from the Internet with Flash Media Server as its destination must pass through an edge server.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.