![]() kcal /h, (6.4)
kcal /h, (6.4)
where Ny - adjusting or rated power of installation, kwatt; 860 - thermal equivalent of 1 kwatt.
![]() kcal /h.
kcal /h.
2. Thermal emissions from candlelight
![]() kcal /h, (6.5)
kcal /h, (6.5)
where Nосв - total power of illumination sources, kwatt
![]() kcal /h.
kcal /h.
3. Thermal emissions by people.
Allocation of heat by people depends on expenses or energy and air temperature in.
![]() , (6.6)
, (6.6)
where n - amount of workers in shop, qл- quantity of heat allocated by people at temperature of air in 20 °С at work of average difficulty, kcal/h.
![]() kcal /h.
kcal /h.
4. Heat receipt through lights due to solar radiation,
![]() kcal /h,
(6.7)
kcal /h,
(6.7)
where F - the area of a light, m2, F=60 m2; q0- quantity of heat, entering by solar radiation through lights, kcal /(h·m2), q0=2,08·103 kcal /(h·m2).
![]() kcal /h.
kcal /h.
Total quantity of thermal emissions
S Q heat generation = Q1 +Q2 +Q3 +Q4 (6.8)
S Q heat generation =221041 kcal /h.
5. The main heat loss occur through construction protections of buildings,
Q heat loss = kF(tп - tн) kcal /h, (6.9)
where k- heat transfer factor of the barrier, kcal /(h·m2·°С); F- barrier surface, m2; F= Fст + Fф; Fст- walls surface, m2, Fст=2520 m2; Fф- lanterns surface, m2, Fф=486 m2; F= 3006 m2; tп- air temperature in the shop, °С, tн- external relative specified temperature, °С.
Q heat loss = (1,06·2520+ 5,5·486)·3= 16033 kcal /h
Q= 221041 - 16033= 205008 kcal /h
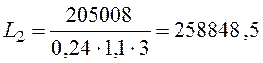 m3/h
m3/h
Lmax= 0,4 L2 (6.10)
Lmax= 0,4 258848,5= 103539,4 m3/h.
We choose the ventilator of low pressure Ц 4-76 №20 of usual performance - for moving nonaggressive environments with temperature not above 80°С, with productivity L= 40000 m3/h and full pressure Рv= 900 MP (hв=0,84).
Required power on the electric motor shaft N, kwatt, is defined under the formula:
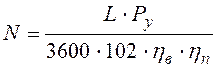 , (6.11)
, (6.11)
where hв= 0,84 - the fan efficiency , hп= 1 - the transfer efficiency .
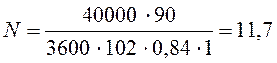 kwatt
kwatt
Adjusting power of electric motor Nу, kwatt, is under the formula:
![]() , (6.12)
, (6.12)
where kз- coverage power factor , kз=1,2.
![]() kwatt.
kwatt.
Quantity of ventilators is calculated under the formula
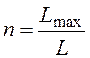 , (6.13)
, (6.13)
where Lmax- maximum quantity of air necessary for creation of normal working conditions, m3/h, L - productivity of the ventilator, m3/h.
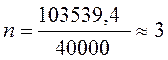 .
.
For preparation and coverings deposition shop 3 ventilators of type Ц4-76 №20 with productivity 40000 м3/ч and electric motor power of 14 kwatt are necessary.
The extreme situation is an infringement of normal conditions of people's vital activity on the object, caused by damage, accident and other dangerous events which can bring to ruin or to defeat of people and significant material losses. Object - a workplace of the operator. Occurrence of extreme situations of technogenic character (a code of sphere of occurrence 10000) can cause:
- Fires and not provoked explosions (10200);
- Sudden destruction of buildings and constructions (10600);
-Accidents on electrical power systems (10700);
- Accidents on life-support systems (10800);
- Accidents on communications and telecommunications (10900).
Primary amazing factors of the technogenic character extreme situation, caused by fires, are: light radiation, smoke blanketing of an environment, chemical environmental contamination.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.