2. The Components of electric equipment which are normally being energized (cases of blocks, electric motors, boards and cases) should be reliably earthed;
3. Periodically to check serviceability of grounding of an electric equipment.
4. At performance of repair work to use the electro tool with the voltage no more than 36 V;
5. In shop with the installation in the electrical safety corner should be following safety means:
a) Dielectric gloves 2 pairs TS 38-106359-79
b) Ground beam 1 piece
c) Dielectric rugs 10 pieces GOST 4997-75
d) Asbestos-tarpaulin flat 1 pieces dimensions 5х5 m
e) The first-aid outfit 1 piece
f) Fire extinguisher OU-5 3 pieces GOST 7276-73
6. To switch off and disconnect the high-voltage equipment only when the dielectric rugs are available;
7. At water stain on electric cases and equipment, cables immediately to disconnect an electric voltage. To work with an electric equipment before full drying.
As during preparation of details surfaces for covering deposition it is used trichloroethylene, the department in which clearing of details is made should have good ventilation and trichloroethylene should be stored in lightproof utensils as illumination accelerates its decomposition.
Sprayed materials vapors are present at the pumped out volume of the chamber. These pairs are pumped out by vacuum system and partially precipitated on constructional details of pumps and pipelines, and partially thrown out in the atmosphere. For clearing pumped out gas it is necessary to use special filters which are installed on exhaust branch pipes of forepumps.
Hygiene and sanitary conditions of the air environment in the working zone of industrial premises should meet the requirements СН 245-80.
At vapor liberation or gassing necessary air exchange is defined proceeding from their dilution up to admissible concentration, м3/ч:
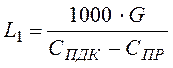 , (6.1)
, (6.1)
where G- quantity of allocated harmful substance, g/h, Спдк- maximum permissible concentration of harmful impurity in the shop air, mg/m3, Спр- concentration of harmful substance in incoming air, mg/m3.
If incoming air does not contain harmful impurity Спр=0 and above resulted formula will become:
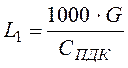 ,
,
where G=150 g/h; Спдк=300 mg/m3 – for trichloroethylene,
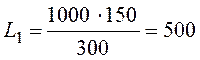 m3/h.
m3/h.
At presence of superfluous heat in working premises quantity of air necessary for creation of normal working conditions, m3/h:
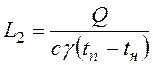 , (6.2)
, (6.2)
where Q – excess heat which is defined by the sum of thermal emissions minus heat loss, kcal/h,
Q= S Qheat generation - S Q heat loss, (6.3)
tп - temperature of air removed from the shop; tн - temperature of the external air entered into the shop; c - the average specific thermal capacity of air equal to 0,24 kcal/(kg °С); g - volumetric weight of air entering into the shop, equal to 1,1 kg/m3.
The quantity of excess heat is composed of heat allocated simultaneously by all sources in shop minus loss of heat.
People, machine tools, machines, industrial thermal installations, lighting devices and solar radiation are sources of allocation in premises of a significant amount of heat.
Heat allocated by these sources can surpass heat loss of premises owing to what in premises the heat surpluses occur, leading to rise in temperature.
The greatest size heat surpluses amount during the summer period of time when heat loss of buildings decrease, and thermal emissions due to solar radiation increase.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.