|
Implementation |
Port route |
||
|
Hardware configuration |
Configure an EFS4 board in NE1 and NE2 respectively to access the Ethernet services of A and B. For slots of the EFS4 board, refer to “Appendix A Network Configuration Requirements”. |
||
|
Service route |
NE1 |
NE2 |
|
|
A |
MAC1 ïð VCTRUNK1 |
VCTRUNK1 ïð MAC1 |
|
|
Bind VCTRUNK1 to five VC-12s |
|||
|
B |
MAC2 ïð VCTRUNK2 |
VCTRUNK2 ïð MAC2 |
|
|
Bind VCTRUNK2 to one VC-3 |
|||
|
Protection |
The service can be protected by the SDH equipment. |
||
& Note:
You can apply the same principles to implementation of GE services except that the GE service requires EGS2 board and binding VCTRUNK to one or more VC-3s.
Adopting point-to-point transparent transmission, the EPL service achieves high security because it occupies the line alone and isolates other services. It is applicable in providing private line for VIPs.
The headquarters of A is in city 1, its M&S department and technical support department are in city 2. The headquarters needs to communicate with two branches over 10 Mbit/s bandwidth respectively. The communication between the headquarters and two branches must be isolated. All the Ethernet switches of A provide 100 Mbit/s Ethernet electrical interfaces. The Ethernet switch in the headquarters supports virtual local area network (VLAN).
The services from two branches need to be transmitted to the headquarters and be converged. The service from the headquarters needs to be transmitted to the two branches. This application can be realized by the OptiX OSN 3500, as shown in Figure 4-2.
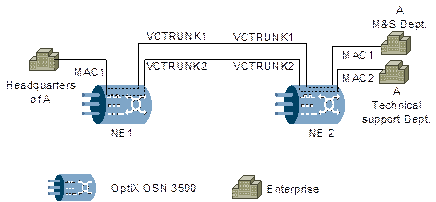
Figure 4-2 EPL service application (convergence)
|
Implementation |
Port route + VLAN route
Service convergence: In city 2, services from two branches are accessed through MAC ports of NE2. After added with different VLANs (VLAN ID: 100 and VLAN ID: 200), services are transmitted to city 1 over different VCTRUNKs. NE1 converges the two lines of services and output them through a MAC port. Service split: The Ethernet processing board of NE1 processes the service (with VLAN ID: 100 and VLAN ID: 200) from the headquarters of A, sends them over different VCTRUNKs to the branches based on the VLAN ID number. |
||
|
Hardware configuration |
Configure an EFS4 board in NE1 and NE2 respectively to access the Ethernet service from the headquarters and the branches of A. For slots of the EFS4 board, refer to “Appendix A Network Configuration Requirements”. |
||
|
Service route |
NE1 |
NE2 |
|
|
Headquarters ïðM&S department |
MAC1 + VLAN ID: 100 ïð VCTRUNK1 + VLAN ID: 100 |
VCTRUNK1 + VLAN ID: 100 ïð MAC1 + VLAN ID: 100 |
|
|
Bind VCTRUNK1 to five VC-12s |
|||
|
Headquarters ïð Technical support |
MAC1 + VLAN ID: 200 ïð VCTRUNK2 + VLAN ID: 200 |
VCTRUNK2 + VLAN ID: 200 ïð MAC2 + VLAN ID: 200 |
|
|
Bind VCTRUNK2 to five VC-12s |
|||
|
Protection |
The service can be protected by the SDH equipment. |
||
& Note:
You can apply the same principles to implementation of GE services except that the GE service requires EGS2 board and binding VCTRUNK to one or more VC-3s.
The MSTP equipment can realize the convergence of the EPL service and point-to-multipoint networking of the Ethernet service. The VLAN label makes it possible that more than one EPL service shares a MAC port, thus saving the port resources.
The VLAN tags of Ethernet services received by NE2 may come from two ways:
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.