Table 5-1 ATM service requirements of each NE
|
No. |
Service requirement |
Source station |
Sink station |
Bandwidth |
|
1 |
Point-to-point |
NE2: Provides 155 Mbit/s POS interface. |
NE1 |
3 x 10 Mbit/s |
|
2 |
Point-to-point |
NE3: Provides 155 Mbit/s POS interface. |
NE1 |
2 x 20 Mbit/s |
|
3 |
Point-to-point |
NE4: Provides 155 Mbit/s POS interface. Provides 34 Mbit/s POS interface. |
NE1 |
1 x 30 Mbit/s 1 x 20 Mbit/s |
The type of ATM service accessed to each NE is CBR.
The ATM service needs protection.
The analysis shows that the total bandwidth of the ATM services converged to the central node NE 1 is (3 x 10 Mbit/s + 2 x 20 Mbit/s + 30 Mbit/s + 20 Mbit/s), that is, 120 Mbit/s. These ATM services can share the bandwidth of a VC-4 in a SDH ring network.
The OptiX OSN 3500 can realize transmitting and converging data services. For ATM services accessed from multiple points, the OptiX OSN 3500 support statistical multiplexing, realizing bandwidth sharing on ring network. Therefore, this example adopts the OptiX OSN 3500 to construct a multi-service transport platform, so as to transmit and converge ATM services. ATM services can be protected by the MSP ring at the SDH layer.
Figure 5-3 shows the networking diagram.
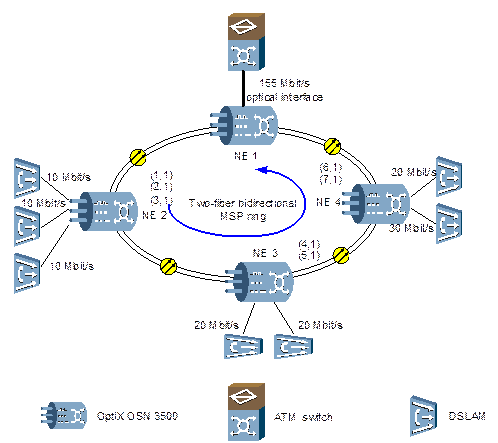
Figure 5-3 Statistical multiplexing of ATM services
The central node NE1 adopts the OptiX OSN 3500 to receive the ATM services from other NEs and transmit them to the ATM switch after convergence.
NE2, NE3, and NE4 are end offices, adopting the OptiX OSN 3500 to receive ATM services from DSLAM and multiplex them statistically into a VC-4 to be transmitted to the central node.
|
Implementation |
Statistical multiplexing: Multiplex the ATM services that NE2, NE3, and NE4 access from DSLAM into a VC-4, converge it to a port of NE1 and transmit it to the upper ATM switch. |
|||
|
Hardware configuration |
Configure an ADQ1 board at NE1 to converge ATM services of other NEs and transmit them to the upper ATM switch through a 155 Mbit/s port. Configure an ADQ1 board at NE2, NE3, and NE4 respectively to access ATM services from DSLAM. Configure ADQ1 and PL3 boards at NE4 to access 34 Mbit/s ATM services and share the bandwidth on the ring. For slots of the ADQ1 board, refer to “Appendix A Network Configuration Requirements”. |
|||
|
Traffic control |
In this example, the type of ATM service is CBR and the traffic parameters PCR and CDVT should be set. |
|||
|
NE1 |
NE2 |
NE3 |
NE4 |
|
|
PCR: 283020 cells/s CDVT: 500ms |
PCR: 23585 cells/s CDVT: 500ms |
PCR: 47170 cells/s CDVT: 500ms |
PCR: 47170 cells/s CDVT: 500ms |
|
|
PCR: 70755 cells/s CDVT: 500ms |
||||
|
Service route |
NE1 |
NE2 |
NE3 |
NE4 |
|
ATM external port 1 (1–7,1) ïð ATM internal port 1 (1–7,1) ïð VC-4 |
10 Mbit/s service 1: ATM external port 1 (1,1) ïð ATM internal port 1 (1,1) ïð VC-4 |
Pass-through service: ATM internal port 1 (1–3,1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (1–3,VC1) ïð VC-4 |
Pass-through service: ATM internal port 1 (1–5,VC1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (1–5,VC1) ïð VC-4 |
|
|
10 Mbit/s service 2: ATM external port 2 (2,1) ïð ATM internal port 1 (2,1) ïð VC-4 |
||||
|
10 Mbit/s service 3: ATM external port 3 (3,1) ïð ATM internal port 1 (3,1) ïð VC-4 |
||||
|
- |
20 Mbit/s service 1: ATM external port 1(4,1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (4,1) ïð VC-4 |
|||
|
Service route |
- |
20 Mbit/s service 2: ATM external port 2 (5,1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (5,1) ïð VC-4 |
||
|
- |
- |
20 Mbit/s service 1: PL3 interface ïð ATM external port 1 (6,1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (4,1) ïð VC-4 |
||
|
- |
- |
30 Mbit/s service 1: ATM external port 2 (7,1) ïð ATM internal port 2 (7,1) ïð VC-4 |
||
|
Note: The ATM external port of ADQ1 is the external optical port used to access the ATM service, while the ATM internal port refers to the logical port used to connect the ATM processing module and the SDH cross-connect module. |
||||
|
Protection |
This example does not use VP-Ring at the ATM layer, so the ATM service is protected by the two-fiber bidirectional MSP ring of SDH. The switching time is no more than 50ms. |
|||
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.