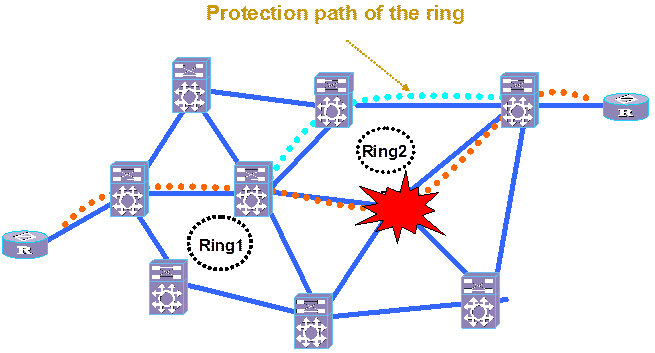
Figure 4-5 Protection for service of gold level
Service of silver level refers to the service with path re-calculated on the real-time converged topology at failure occurrence. As the network convergence is time-taking, the service damaging or interruption time in re-routing is longer than the switching time for the above two services.
Compared with the two services described above, the advantage of the silver service lies in that it does not need bandwidth reservation for recovery, thus much improving the bandwidth availability. As shown in Figure 4-6, when the service link fails, a new path will be found out to recover the service.
There are two modes for re-routing: revertive and non-revertive. If the service is restored to the original path when the fault is removed, it is in revertive mode; if not, it is in non-revertive mode.
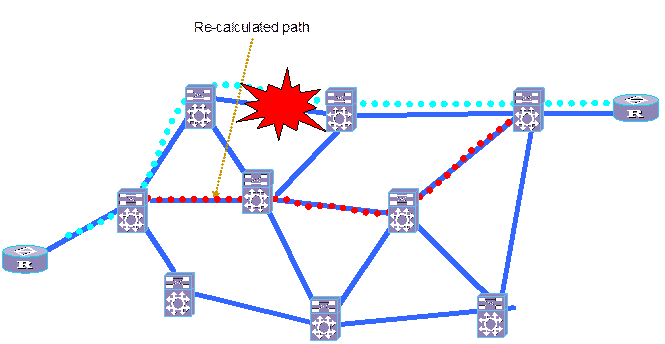
Figure 4-6 Application of silver level
Provision of multiple-leveled services inherits merit of fast protection switching of the SDH ring network on the one hand, and takes fully advantages of bandwidth availability of the mesh network on the other hand.
4.4.2 Automatic End-to-End Service Configuration
The end-to-end service can be rapidly generated and protected by some simple operations listed below through the NM.
n Select source node.
n Select destination node.
n Select desired bandwidth.
n Select service level.
n Auto-establish service connection.
4.4.3 Mesh Networking
Compared with the ring network, the mesh network take advantages of bandwidth availability, network scalability, and survivability. This network topology is suitable for the area with large and evenly distributed traffic. Mesh network achieves a higher reliability because there are multiple routes available between two nodes. This effectively protects the traffic against node congestion and node failure. The one shown in Figure 4-6 is a mesh networking configuration.
4.4.4 Traffic Engineering
The traffic engineering control technique of the OptiX OSN 9500 allows a load-balance traffic networkwide for convenient network planning and improved bandwidth availability.
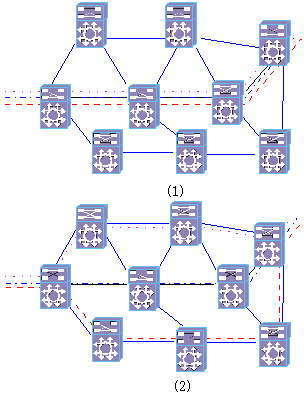
|
(1) Network without traffic engineering |
(2) Network with traffic engineering |
Figure 4-7 Traffic engineering technique in application
As shown in Figure 4-7, the intelligent network featuring traffic engineering control can:
n Route not to the congested path and node.
n Route not to the high-risk path and node.
n Automatically make load-balance traffic networkwide.
n Share the service load.
4.4.5 Integrated Intelligent Service request
Generally, the intelligent service of the OptiX OSN 9500 is an integrated application of the above intelligent feature, including SLA service, traffic engineering, mesh networking and end-to-end service which can be point-and-configure in the NM.
n Dynamic apply service (SLA-supporting).
n Configure end-to-end service by pointing on the NM system.
n Calculate requirement-satisfying best service path based on traffic engineering. Main technology adopted: CSPF.
n Establish GMPLS signaling connection on the service path. Main technology adopted: RSVP-TE and CR-LDP.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.