


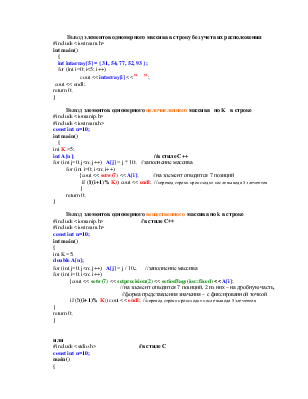






























Для ввода, вывода и обработки массивов используются циклы. Ввод массива реализуется вводом в цикле значений его элементов, например:
#include <stdio.h> //в стиле С
const int n=5;
main()
{ int A[n];
for (int i=0; i <n; i++) {printf (”input A[%d]\n”, i); scanf (”%d”, &A[i]); } return 0;
}
#include <iostream.h> //в стиле С++
const int n=5;
main()
{ int A[n];
for (int i=0; i <n; i++) {cout << "Enter A[" <<i << “] “ << endl;
cin >> A[i];
} return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными целыми положительными значениями от 0 до 32767:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
const int n=20;
main()
{
int Random_array[n]; for (int index =0; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index] = rand();
cout << Random_array[index] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными целыми положительными или отрицательными значениями от -16384 до 16383:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
const int n=20;
main()
{
int Random_array[n]; for (int index =0; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index] = rand()-16384;
cout << Random_array[index] << endl; }
return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными вещественными значениями от 0.0. до 1.0:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
const int n=20;
main()
{
double Random_array[n]; for (int index =0; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index]= rand ()/32767.0;
cout << Random_array[index] << endl; }
return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными возрастающими (не убывающими) целыми значениями:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
#include <time.h>
main ()
{
const int n=10;
int Random_array[n];
srand (time(0)); //отсчет от календарного времени в секундах !!!
Random_array [0]= rand()/1000; //значение от 0 до 32
cout << Random_array[0] << endl;
for (int index =1; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index]= Random_array [index-1]+rand()/1000;
cout << Random_array[index] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными целыми значениями из диапазона [a, а+b]:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
main ()
{
const int n=10;
int Random_array[n];
int a=5, b=10;
for (int index =0; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index] = a + rand() % b;
cout << Random_array[index] << “ “;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Инициализация массива размерности n случайными целыми значениями из диапазона [-a, b-a]:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
main ()
{
const int n=10;
int Random_array[n];
int a=5, b=10;
for (int index =0; index < n; index++)
{Random_array [index] = -a + rand() % b;
cout << Random_array[index] << “ “;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Задание элементов массива можно построить по некоторому правилу, например: #include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
main ()
{
const int n=10;
double A[n];
for (int j=0; j<n; j++) {if (j%2) A[j] = j * 10.; else A[j] = j/100.; cout << A[j] << ” ”; }
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
получим массив:
0 10 0.02 30 0.04 50 0.06 70 0.08 90
Вывод элементов массива также можно организовать по-разному.
Вывод элементов одномерного массива по одному в строке:
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
int intarray[5] = { 31, 54, 77, 52, 93 };
for(int j=0; j<5; j++)
cout << intarray[j] << endl;
return 0;
}
Вывод элементов одномерного массива в строку без учета их расположения:
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
int intarray[5] = { 31, 54, 77, 52, 93 };
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) cout << intarray[i] << ” ”; cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Вывод элементов одномерного целочисленного массива по K в строке #include <iomanip.h>
#include <iostream.h>
const int n=10;
int main()
{
int K =5;
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.