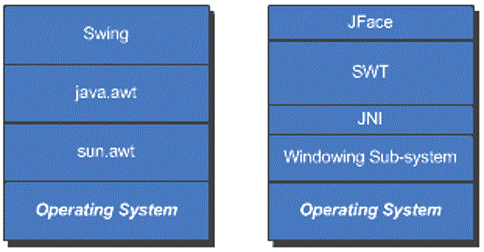
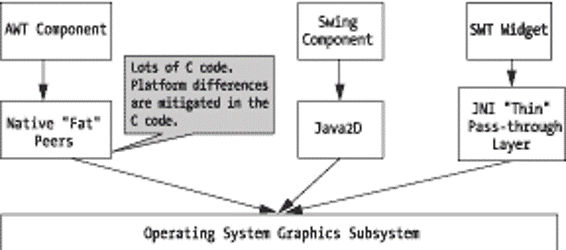
SWT & JFace
1
2
Подключаем SWT
-
org.eclipse.swt_3.5.2.v3557f.jar
-
org.eclipse.swt.win32.win32.x86_3.5.2.v3557f.jar
3
"Hello, World" in SWT
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
Shell shell = new Shell(display);
Label label = new Label(shell, SWT.CENTER);
label.setText("Hello, World");
label.setBounds(shell.getClientArea());
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) display.sleep();
}
display.dispose();
} }
4
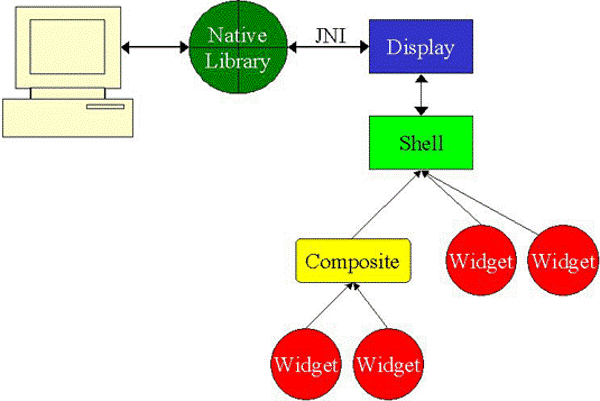
5
Создание элементов SWT
-
Всегда создаётся пара объектов
-
Label label = new Label(shell, SWT.CENTER);
-
//что решает ряд проблем, например (MFC)
-
CButton button; // Construct the C++ object on the stack CString str = _T("Hi"); // Create a CString to text button.SetWindowText(str); // Set the button text-PROBLEM!
-
button.Create(…); // Creates the Windows widget
-
Родительский эл. и стиль
-
Label label = new Label(shell, SWT.CENTER);
6
Освобождение ресурсов в SWT
-
Rule 1 : If You Created it, You Dispose It
-
Color color1 = new Color(display, 255, 0, 0);
-
………….
-
Rule 1 says you created it, so you must dispose it when you are done using it, like this:
-
color1.dispose();
-
However, if you don't call a constructor to get a resource, you must not dispose the resource:
-
Color color2 = display.getSystemColor(SWT.COLOR_RED);
-
…………..
7
-
Rule 2 : Disposing the Parent Disposes the Children
-
// Create the text field
-
Text text = new Text(shell, SWT.BORDER);
-
// Create the new font
-
Font font = new Font(display, "Arial", 14, SWT.BOLD);
-
// Set the font into the text field
-
text.setFont(font);
-
???.dispose();
8
-
Rule 3 : Ignoring Disposed Objects
-
org.eclipse.swt.SWTException: Widget is disposed at org.eclipse.swt.SWT.error(SWT.java:2332) at org.eclipse.swt.SWT.error(SWT.java:2262) at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Widget.error(Widget.java:385) at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control.getDisplay(Control.java:735) at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Widget.isValidThread(Widget.java:593) at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Widget.checkWidget(Widget.java:315) at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text.getText(Text.java:705) at Broken.main(Version.java:24)
9
Display object
-
void asyncExec(Runnable runnable)
-
Gives non-user-interface threads the ability to invoke the protected functions of the SWT widget classes. The user-interface thread performs the code (invokes the run() method) of the runnable at its next "reasonable opportunity." This function returns immediately.
-
void syncExec(Runnable runnable)
-
Like asyncExec(), but this function returns after the run method of the Runnable object returns.
-
void update()
-
Causes all pending paint requests to be processed.
-
static Display findDisplay (Thread thread)
-
Given a user-interface thread, this function returns the associated Display object. If the given thread isn't a user-interface thread, this method returns null.
10
Shell object
-
BORDER - Adds a border.
-
CLOSE - Adds a close button.
-
MIN - Adds a minimize button.
-
MAX - Adds a maximize button.
-
NO_TRIM - Creates a Shell that has no border and can't be moved, closed, resized, minimized, or maximized. Not very useful, except perhaps for splash screens.
-
RESIZE - Adds a resizable border.
-
TITLE - Adds a title bar.
-
DIALOG_TRIM = TITLE | CLOSE | BORDER.
-
SHELL_TRIM = CLOSE | TITLE | MIN | MAX | RESIZE.
-
APPLICATION_MODAL - Creates a Shell that's modal to the application.
-
PRIMARY_MODAL - Creates a primary modal Shell.
-
SYSTEM_MODAL - Creates a Shell that's modal system-wide.
-
MODELESS - Creates a modeless Shell.
11
Менеджеры расположения
-
FillLayout - This layout arranges components horizontally on a row or vertically on a column (BoxLayout)
-
RowLayout - Similar to FillLayout but more flexible, allowing multiple rows, fill, wrapping, and custom spacing (FlowLayout)
-
GridLayout - Lays components on a grid; offers many options for fine-grained control (GridBagLayout)
-
FormLayout - Relative layout that uses attachments to a container edge or a sibling widget's edge (Нет аналога)
-
StackLayout - Stacks components, only top component is visible (CardLayout)
-
null layout - You can place controls absolutely.
12
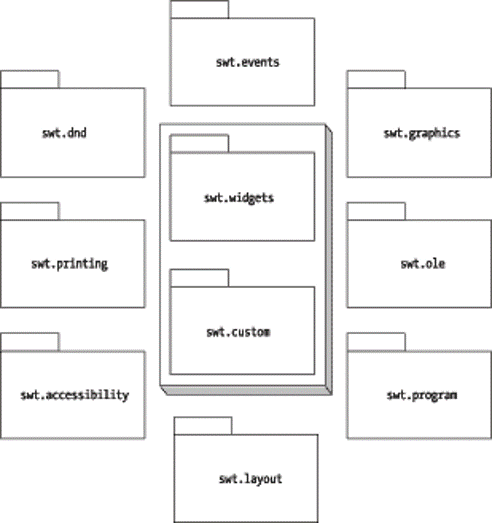
13
Untyped Listeners
-
Listener interface, contains one method:
-
void handleEvent(Event event)
-
Add an untyped listener to a widget:
-
void addListener(int eventType, Listener l)
-
button.addListener(SWT.Selection, new Listener() { public void handleEvent(Event e) {
-
switch (e.type) {
-
case SWT.Selection:
-
System.out.println(“pressed");
-
break;
-
} } };
14
Typed Listeners
-
ControlListener - Listens for move and resize events
-
DisposeListener - Listens for dispose events
-
FocusListener - Listens for focus gained and lost events
-
HelpListener - Listens for help requests
-
KeyListener - Listens for key presses and releases
-
MenuListener - Listens for menu events
-
ModifyListener - Listens for text modifications
-
MouseListener - Listens for mouse button presses
-
MouseMoveListener - Listens for mouse movements
-
MouseTrackListener - Listens for when the mouse enters
-
PaintListener - Listens for paint events
-
SelectionListener - Listens for selection events (for example, button clicks)
-
ShellListener - Listens for shell events
-
TraverseListener - Listens for traverse events
-
TreeListener - Listens for tree events
-
VerifyListener - Listens for, and potentially intercepts, text modifications
15
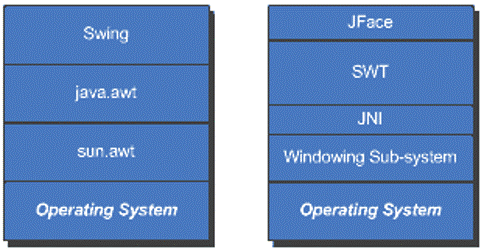
16
-
JFace:
-
Provides Viewer classes that handle the tedious tasks of populating, sorting, filtering, and updating widgets
-
Provides Actions to allow users to define their own behavior and to assign that behavior to specific components, e.g. menu items, tool items, push buttons, etc.
-
Provides registries that hold Images and Fonts
-
Defines standard dialogs and wizards, and defines a framework for building complex interactions with the user
17
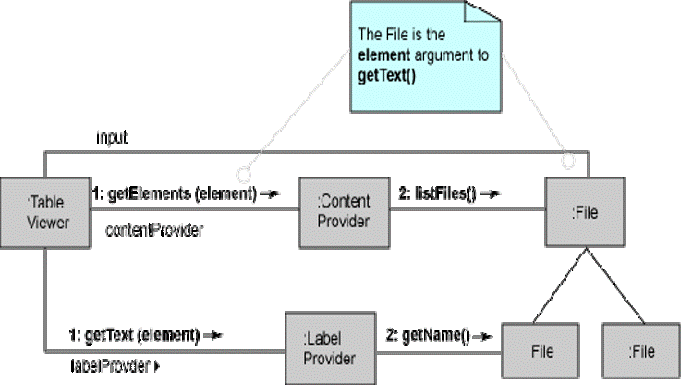
18
-
Window: The org.eclipse.jface.window package provides window creation and management facilities. Of particular interest is the ApplicationWindow class, which provides a higher-level application window and encapsulates the SWT event loop.
-
Viewers: The org.eclipse.jface.viewers package provides a framework of viewers such as TreeViewer and TableViewer, which are model-driven components that make use of SWT widgets and adapt content of a model to the widget.
-
Dialogs: The org.eclipse.jface.dialogs package provides several commonly used dialog boxes.
-
Actions: The org.eclipse.jface.actions package provides a UI action framework that's similar





