Contents
1 NE Type and Networking Capability 1-1
1.1 NE Description 1-1
1.1.1 TM 1-1
1.1.2 ADM 1-2
1.1.3 MADM 1-4
1.2 Networking and Grooming Capability 1-6
1.2.1 Networking Capability 1-6
1.2.2 Grooming Capability 1-9
Figures
Figure 1-1 Functional block diagram of TM 1-1
Figure 1-2 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-16 TM 1-2
Figure 1-3 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-64 TM 1-2
Figure 1-4 Functional block diagram of ADM in the OptiX OSN 3500 1-3
Figure 1-5 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-16 ADM 1-3
Figure 1-6 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-64 ADM 1-4
Figure 1-7 Functional block diagram of MADM in the OptiX OSN 3500 1-4
Figure 1-8 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-64 MADM 1-5
Figure 1-9 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-16 MADM 1-5
Figure 1-10 Hybrid network of the OptiX OSN 3500 and other equipment 1-8
Figure 1-11 Hybrid network of the OptiX OSN 3500, OptiX 10G and OptiX Metro 3000 1-9
Figure 1-12 Grooming capability of the OptiX OSN 3500 1-10
Tables
Table 1-1 Maximum networking capability and configuration in interconnecting node 1-6
Table 1-2 Service access capability of OptiX OSN 3500 1-10
This chapter introduces the NE types of the OptiX OSN 3500, as well as the networking and grooming capabilities of the product.
There are three types of NEs in the optical transmission network:
n Terminal multiplexer (TM)
n Add/Drop multiplexer (ADM)
n Multiple add/drop multiplexer (MADM)
The main function of TM is to multiplex low-rate plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) signals into high-rate SDH signals, cross-connect line signals with tributary signals, as well as to demultiplex high-rate SDH signals to low-rate PDH signals. Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram of TM.
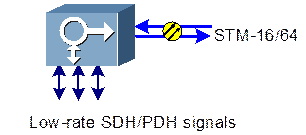
Figure 1-1 Functional block diagram of TM
TM is used as the terminal of a point-to-point network, a chain network or the interconnecting node of a ring with chain network.
Figure 1-2 shows the hardware configuration when the OptiX OSN 3500 serves as an STM-16 TM. Insert an SL16 board in any one of slots 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, and 13 to transmit and receive STM-16 optical signals. Configure other boards in other slots according to service requirements.
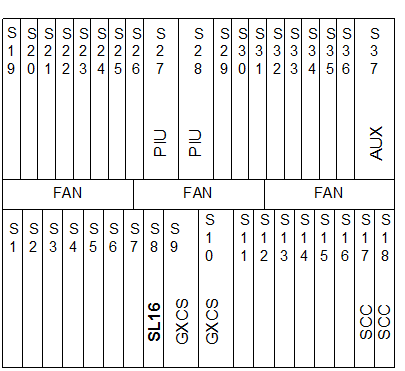
Figure 1-2 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-16 TM
Figure 1-3 shows the hardware configuration when the OptiX OSN 3500 serves as an STM-64 TM. Insert an SL64 board in any one of slots 7, 8, 11, and 12 to transmit and receive STM-64 optical signals. Configure other boards in other slots according to service requirements.
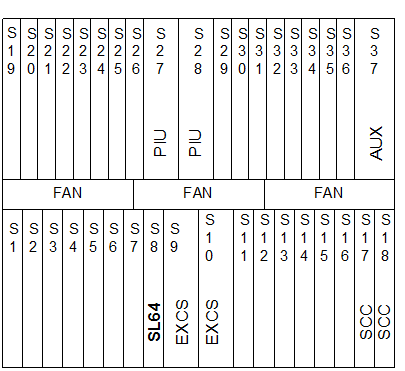
Figure 1-3 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-64 TM
The ADM is most widely used in the network. It can flexibly add/drop any tributary signals by integrating synchronous multiplexing and digital cross-connection functions into a whole. Besides the functions of TM, ADM also provides the cross-connection of line signals and between line signals and tributary signals. For example, the accessed E1 tributary signal can be multiplexed and connected to line signals of two directions, and the line signals of two directions can be interconnected.
The structure of ADM is similar to two back-to-back TMs, as shown in Figure 1-4.
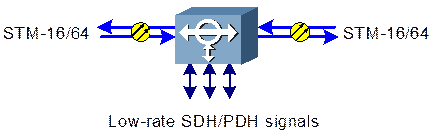
Figure 1-4 Functional block diagram of ADM in the OptiX OSN 3500
ADM is widely used in chain, ring and HUB networks.
Figure 1-5 shows the hardware configuration when the OptiX OSN 3500 serves as an STM-16 ADM. Insert two SL16 boards in any two of paired slots 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, and 13 to transmit and receive STM-16 optical signals of two directions. Configure other boards in other slots according to service requirements.
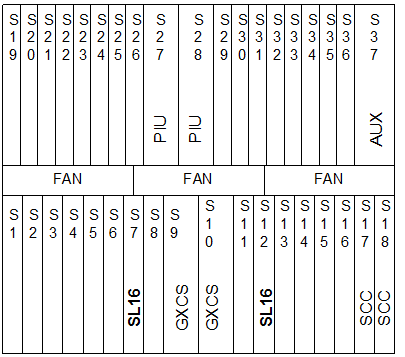
Figure 1-5 Hardware configuration of the OptiX OSN 3500 when serves as an STM-16 ADM
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.