Usually, public services are a kind of converged service of high capacity and relatively low QoS level. If it is transmitted by the Ethernet Layer 2 switching processing board, the following problems may occur:
n In the Layer 2 shared ring mode, all services can share the bandwidth. However, once a node encounters large volume of traffic, the traffic of other nodes cannot be assured.
n If the bandwidth of each node is limited, it is impossible to realize bandwidth sharing.
n The Ethernet service is protected at the SDH layer, which requires extra bandwidth.
RPR is a loop technology based on dynamic bandwidth sharing and is a perfect solution to transmit public service (lower priority) in big granularity. It not only realizes flow equalization among nodes through the fairness algorithm, but also improves the bandwidth utilization. In addition, it provides the Ethernet ring protection with the switching time less than 50ms. This kind of protection does not need to occupy the bandwidth.
The Ethernet processing board of the OptiX OSN 3500 supports the following data protection functions:
n TPS protection for FE service
n Link capacity adjustment scheme (LCAS)
n Committed access rate (CAR)
n Rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP)
n Flow control
n Resilient packet ring (RPR)
The OptiX OSN 3500 supports 1:1 TPS protection for electrical fast Ethernet (FE) service, namely, 1:1 TPS protection for the EFS0 board. Figure 4-10 shows the principle of 1:1 TPS for the FE service.
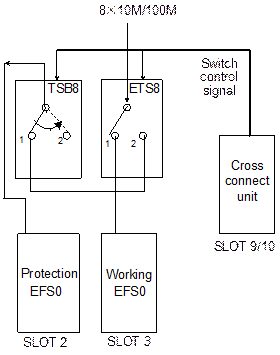
Figure 4-10 The TPS principle of the EFS0
When each working board is working normally, the service signal is accessed to the EFS0 directly through position 1 of the control switch on the ETS8.
When the failure of working EFS0 in slot 3 is detected, the control switch of the corresponding ETS8 switches from position 1 to position 2 to realize protection of the working board in slot 3 by the protection board in slot 2.
LCAS provides an error tolerance mechanism, enhancing the reliability of concatenation. It has the following functions:
n Configure the system capacity, add or reduce the number of VC involved in the concatenation and change the service bandwidth dynamically without damaging the service.
n Protect and recover failed members.
As shown in Figure 4-11, LCAS can add or delete members to increase or decrease the bandwidth dynamically without affecting the service.
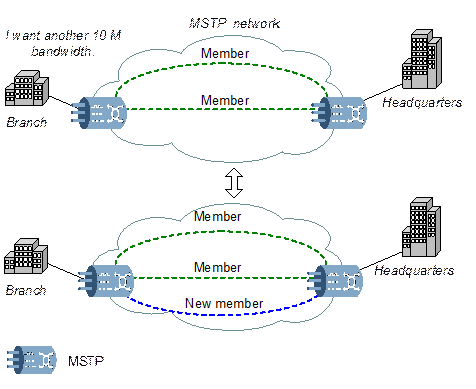
Figure 4-11 LCAS adjusts bandwidth dynamically
As shown in Figure 4-12, LCAS can protect the Ethernet service. When some members fail, the failed members will be deleted automatically. While other members remain transmitting data normally. When the failed members are available again, they will be recovered automatically, and the data will be loaded to them again.
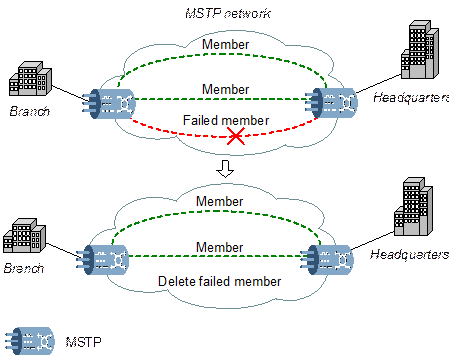
Figure 4-12 LCAS protects the concatenation group
CAR is an important and effective way to manage bandwidth in IP network. The OSN product supports the CAR function of MAC port on the Ethernet board, that is, it supports rate restriction and setting of priorities.
CAR manages the bandwidth by limiting the volume of traffic to/from the network at the peripheral interface. The service is transmitted if the rate is lower than the specified parameter. Otherwise, the part over the specified parameter is discarded or transmitted with lower priority.
For Ethernet services with VLAN label, the priority of the Ethernet packet can be set by CAR.
The system enables RSTP and modifies the network topology logically to avoid the network storm.
RSTP is only applicable in the Ethernet ring.
The Ethernet interface supports IEEE 802.3X flow control, minimizing the packet loss caused by congestion. As shown in Figure 4-13, the node connecting with Ethernet in duplex mode sends PAUSE frame to ask the receiving node to stop transmitting frame signals within a pause-time (N seconds), so as to avoid frame loss.
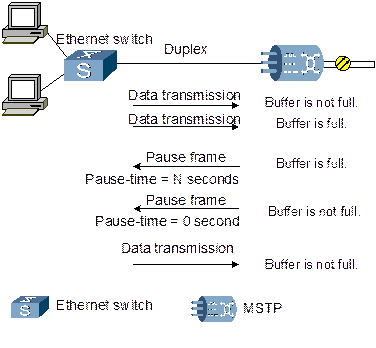
Figure 4-13 Flow control at the Ethernet side
The OptiX OSN product supports IEEE 802.17-specified RPR. RPR is applicable in a ring network to recover the Ethernet service from fiber-cut and link faults as soon as possible.
Figure 4-14 shows a bidirectional RPR with rings of converse directions. Both the outer ring and the inner ring transmit data packets and control packets. The control packet of the inner ring carries the control information of the data packets in outer ring, and it is the same with the order reversed.
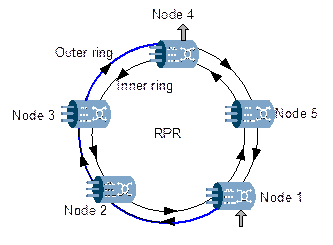
Figure 4-14 Bidirectional RPR
Upon fiber-cut, RPR can start wrapping and packet steering function. Wrapping is to connect the outer ring with the inner ring at the two nodes adjacent to the fiber-cut point, as shown in Figure 4-15. Packet steering is to transmit the packet in the opposite direction at the transmitting node, as shown in Figure 4-16. In either way, the packet can reach the destination from the opposite direction and the fail time is less than 50ms. OptiX OSN 3500 performs Wrapping for general protection switching at the beginning, and then performs Steering when the new topology and service path are established. Then no packet will be lost during protection switching and the switching time is shortened.
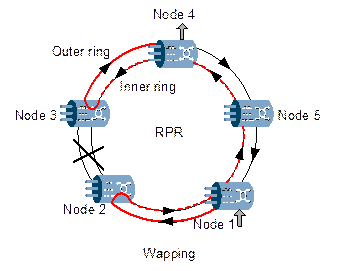
Figure 4-15 Wrapping of RPR
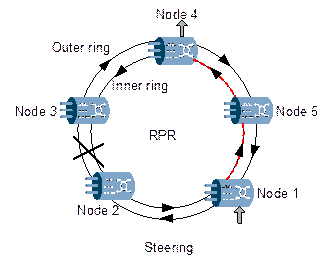
Figure 4-16 Steering of RPR
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.