![]()
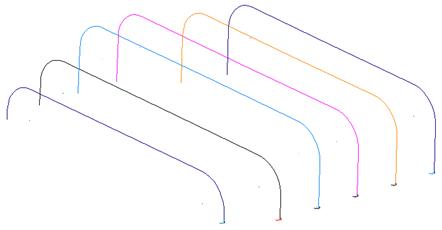
· Blank (Ctrl + K) everything apart from the wireframe shown.
· Select all of the drive curves and select Edit èConvert è Wireframe to Composite Curve.
· Select all of the arcs and select Edit èConvert è Wireframe to Composite Curve.
· Create drive curve surfaces from the composite curves, using Apply on the form rather than Accept until finished.
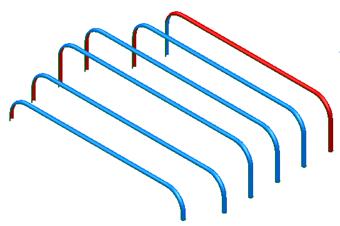
The new surfaces are shown.
· Select and use the Right Mouse button menu to reverse any red surfaces.
· Unblank (Ctrl + L).
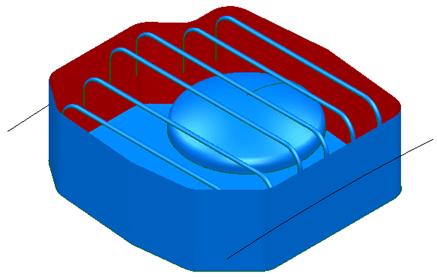
The pump project can now be saved.
· Select Fileè Save and Select File è Close.
 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
 |
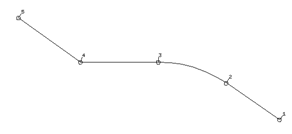
The curve that joins each point on the laterals together to create the surface is known as a longitudinal.
· Create a workplane at 0
· Create a continuous line from the workplane, 10mm in Y, 10mm in X, and 10mm in -Y to produce the 'n-shape'
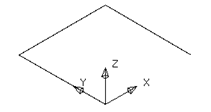
This section will be the basic for the other sections so it will be copied up the Z-axis as individual lines.
· Select the three lines.
· From the Edit toolbar, select Move/Copy Object.
![]()
· Enter 2 for the number of copies and the value of 0 0 5 in the position window, giving you three sets of lines.
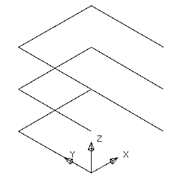
![]() Each set of lines will be filleted by a different radius.
Each set of lines will be filleted by a different radius.
· Create a fillet radius of 1mm on the bottom lines, at each corner.
· Create a fillet radius of 2mm on the middle lateral, at each corner.
· Create a fillet radius of 3mm on the top lateral, at each corner.
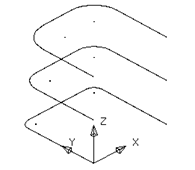
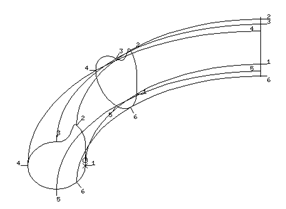
Each shape needs to be turned into a composite curve before a surface can be made.
· Select all of the wireframe and select Edit èConvert è Wireframe to Composite Curve.
· Select the lower composite curve and copy it up the Z-axis by 20mm.
· Select the second from bottom composite curve and copy it up the Z-axis by 10mm.
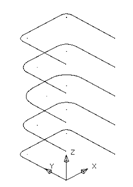
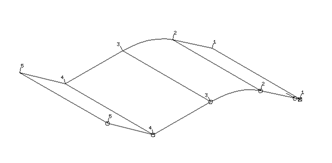
All of the shapes have been turned into composite curves, ready for surface generation. Each of the composite curves will be turned into a lateral on the surface.
· Select all of the composite curves.
· ![]() From the surface menu
From the surface menu ![]() select
Create surface from separate curves.
select
Create surface from separate curves.
A preview of the surface is shown.
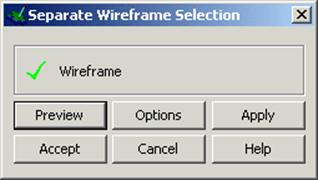
This form allows you to try different options of joining the laterals together with a very useful Preview setting. The default option gives a smooth result, but if a different surface is required other options can be tried.
· Accept the form
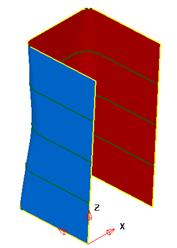
The surface is complete.
· Select File è Close and select Yes.
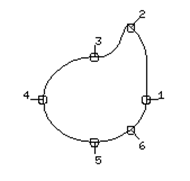
Using the pump example we can use the two curves to make a surface from laterals.
· Open the model pump-project2.
· Blank everything apart from the two long curves.
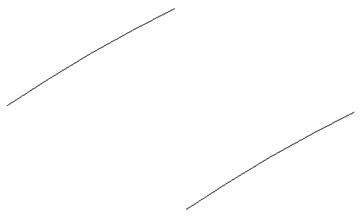
These do not need to be converted into composite curves, as each curve is already a single item.
· Select both curves.
· ![]() From the surface menu
From the surface menu ![]() select
Create surface from separate curves.
select
Create surface from separate curves.
· Select Unblank
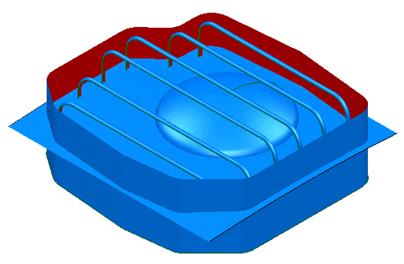
The new surface is shown. It can now be limited to the side wall to produce a trimmed top and trimmed side wall.
· Select and Blank all of the wireframe.
· Limit the curved top surface to the side extrusion.
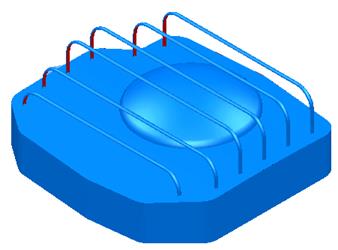
The side wall and top has been trimmed. The dome surface needs trimming to the top.
· Limit the dome surface to the top surface.
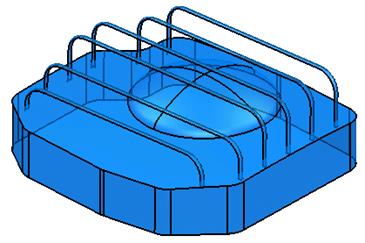
The top and the dome have been trimmed back.
· Select Fileè Save and Select File è Close.
A surface from net is one that lies on a network of curves that are transformed into laterals and longitudinals. A network of any number of curves with at least four sides can be used, and the curves may also extend beyond the outer edge of the surface, provided they do not cross outside this range.
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.