· normalization of new one-dimensional array is performed to achieve zero expectation value and unit standard deviation.
When running pattern recognition modeling following actions are always performed:
· preprocessing of stored patterns;
· definition of initial vector-prototypes, corresponding to stored patterns and adjacent to them vectors;
· preprocessing of input pattern;
Further, depending on model type, process of pattern recognition is modeled.
In case of fully connected network (fig.1) during given time interval system (1) is evaluated.
In the case of third-layer network following actions are performed:
· calculating of initial values of order parameters according to eq. (6)
· modeling of order parameters dynamics i.e. evaluating (5) during given time interval
In purposes of visualization plots of order parameters dynamics and evolution of changing output pattern are shown after modeling.
For each of stored pattern there is capability to set attention parameters, taking into account some priority in recognition.
The main window of program is presented on figure 3.
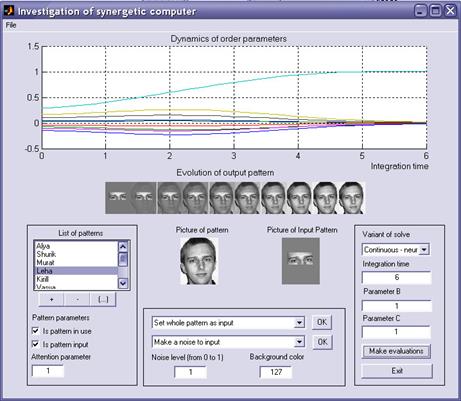
Figure 3. Main window of program, which was used for modeling pattern recognition in synergetic computer
3.2. Example of human faces pattern recognition
As the main recognizable patterns there was used set of face pictures, presented on the figure 4.
These pictures were stored in synergetic computer memory. After that process of recognition was modeled for different initial input images-patterns.





1 2 3 4 5




6 7 8 9
Figure 4. Set of pictures, corresponding to faces, which were used as recognizable patterns
|


|


|


|


![]()
![]()
Input images Evolution of output images
Figure 5. Evolution of recognizable pattern when input image is: noisy (a),
partially set (b), noisy and partially set (c), ambiguous (d)
On figure 5 there are presented examples of pattern recognition with different input images. From this examples one can see, that synergetic computer is able to recognize both noisy and partially set patterns.
When setting ambiguous patterns it is natural to specify attention parameters so to give synergetic computer instructions, which patterns are to be recognized most likely. So one form of control of pattern recognition becomes apparent.
4. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
Synergetic computer represents a powerful tool for recognizing of static patterns. By its abilities for recognizing noisy, partially set patterns it greatly exceeds alternative solutions. Applications of synergetic computer in systems of biometric identification [4] and optical recognition [5] confirms its wide abilities.
Future investigations are planned to be made in several directions. One of them is investigation of invariant image recognition by synergetic computer [6].
Other direction is synergetic computer abilities investigation of expanded pattern recognition at the expense of attention parameters manipulating. Particularly, one can give some examples of such recognition [7]:
· associative recognition chains, when “forgotten” pattern triggers initiate right recognition by “instruction” on the next pattern;
· reproduction of pattern consequences using some initial pattern (prediction task)
5. REFERENCES
[1] H.Haken, Principles of Brain Functioning, Moscow: PER SE, 2001, pp. 245-280 (in Russian).
[2] M.Perus, Mathematical models of associative neural networks, Saint-Petersburg: Karo, 2000 (in Russian).
[3] H.Haken, R.Haas, W.Banzaaf, A new learning algorithm for synergetic computers, Biological Cybernetics, vol.62, 1989, pp. 107-111
[4] R.W. Frischholz, U. Dieckmann, BioID: A multimodal biometric identification system, IEEE, February 2000, pp. 64-68
[5] Jun Gao, Jie Bao, Dingguo Chen, Youqing Yang, Xuedong Yang, Optical-electronic shape recognition system based on synergetic associative memory, SPIE, Volume 4305, 2001, pp. 138-148.
[6] A. Fuchs, H.Haken, Pattern recognition and associative memory as dynamical processes in a synergetic system, Biological Cybernetics, vol. 60, № 1, 1988, pp. 17-22.
[7] A.A.Yudashkin, Bifurcations of stationary solutions in synergetic neural network and control of pattern recognition, Automation and Telemechanics, vol.11, 1996, pp. 139-147 (in Russian).
Уважаемый посетитель!
Чтобы распечатать файл, скачайте его (в формате Word).
Ссылка на скачивание - внизу страницы.